If used improperly, electricity can pose a threat to the environment, health and life of the person. To exclude such cases, the rules for the use of electricity (PUE, national and international standards) have been enacted, which oblige all power circuits to provide protective devices. Among these elements are circuit breakers. To choose them correctly, you need to understand the characteristics that are reflected in the labeling.
General information about machines
As a rule, the machine contains three types of circuit breaker: thermal, electromagnetic and mechanical. The first is designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent, the second - from short circuit in load circuits, the third - for operational switching of electrical circuits.
There are electrical machines that perform protective functions against overload and electric shock (ET). These are switches controlled by differential current with built-in protection against current overloads - difavtomaty (LW).
Main technical characteristics of circuit breakers (AB)
Nominal voltage - the value set by the manufacturer at which the operability of the AB is determined.
Rated current - the current set by the manufacturer, which AB is able to conduct in continuous mode, at which the main contacts remain closed at the specified control ambient temperature (standard +30 ° C).
The breaker frequency is the industrial frequency for which the device is designed and to which the values of other characteristics correspond.
The rated maximum breaking capacity is the ET value, which can disable the AB, while maintaining its performance.
The current limit class is characterized by the tripping time between the start of the circuit breaker opening and the end of the arc time. There are three classes of current limitation:
- Class 3 shutdown time occurs within 2.5 - 6 ms;
- 2 classes - 6–10 ms;
- Grade 1 - more than 10 ms.
The protective characteristic AB determines the limits of the time during which the switching element must trip at a certain value of the ET flowing through it.
There are several types of protective (time-current) characteristics of AB, the most popular are B, C and D
| Type of protective characteristic | Range of instantaneous tripping currents reduced to rated current AB | Appointment |
| A | from 1,3In | To protect circuits in which temporary overcurrents cannot occur during normal operation. |
| AT | from 3in to 5in | To protect circuits in which minor temporary current overloads are allowed in normal operation. |
| WITH | from 5in to 10in | To protect circuits in which moderate temporary current overloads are allowed in normal operation. |
| D | from 10in to 20in | To protect circuits with significant temporary current overloads in normal operation. |
| K | from 12 In | To protect industrial circuits using inductive load. |
| Z | from 4 In | To protect industrial circuits using industrial electronics as a load. |
Differential circuit breakers
The rated breaking differential current IΔn is the value of the breaking differential current specified by the manufacturer at which the motor should operate under specified conditions.
The rated non-disconnecting differential current IΔn0 is the value of the non-disconnecting differential current specified by the manufacturer at which the motor does not operate under specified conditions.
Nominal differential maximum switching on and off ability IΔm0 is the effective value of the variable component of the expected differential current, which the DV can turn on, conduct and turn off.
DV are of three types:
- S - with delayed response time for differential current.
- AC - triggered by a sinusoidal alternating differential current, either applied abruptly or slowly growing.
- AND - provides tripping with differential sinusoidal alternating current and differential pulsating direct current applied abruptly or slowly growing.
Marking machines
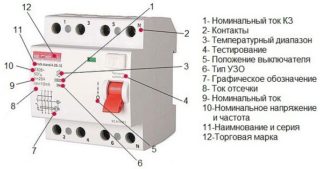
Each machine has its own marking, which is an alphanumeric and conditional graphic images used to identify and bring to the consumer its basic technical characteristics. They are necessary for the correct selection and further operation of the machine.
- manufacturer name or trademark;
- designation of type, catalog number or series number;
- rated voltage value;
- rated current values without the symbol “A” with the previous designation of the type of protective characteristic (A, B, C, D, K, Z) and current limiting class;
- rated frequency value;
- value of the rated maximum breaking capacity in amperes;
- connection diagram, if the correct connection method is not obvious;
- value of the control ambient temperature, if it differs from 30 ° С;
- degree of protection, if only it differs from IP20;
- for type D circuit breakers, the maximum value of the instantaneous trip current, if it is higher than 20In;
- rated impulse withstand voltage Uimp.
The marking of the difavtomats is similar to the marking of AB, but contains additional information:
- rated breaking differential current;
- settings of the tripping differential current (for a DW with several values of the tripping differential current);
- rated maximum differential switching and disconnecting ability;
- a button with the symbol "T" for operational control of the efficiency of the active current by differential current;
- the symbol "~" - for AS type AC;
- symbol for A type A.
Decoding of circuit breakers
Along with the marking of switches, the necessary information about the characteristics and type of AB contains its symbol, which is required to place an order for the purchase of AB.
The symbol of the circuit breaker is as follows: VA47-Х1-Х2Х3Х4ХХ5-УХЛ3
Explanations for the designation AB are given in the table.
| Symbol | Decryption |
| BA47 | Series designation |
| X1 | Switch type |
| X2 | Number of poles |
| X3 | The letter "N" in the presence of a pole without a trip |
| X4 | Type of protective characteristic |
| Xx5 | Rated operational current |
| UHL3 | Designation of a climatic modification and category of placement (in accordance with GOST 15150) |
Examples of notation AB:
- single-pole circuit breaker with type C protection characteristic for a rated current of 16 A: VA47-29-1S16-UHL3 switch
- four-pole circuit breaker with type C protection characteristic with an unprotected pole for a rated current of 100 A: VA47-100-4NC100-UHL3 switch.
For products of UHL3 design, the operating temperature range is from minus 60 to +40 ° C.
Each machine mounted in the switchboard is marked in accordance with its functional purpose. For example, the room number, the designation of the feeder, equipment, etc. to protect the electrical circuits of which this machine is installed.
Tips for choosing a circuit breaker
 There are two main criteria for choosing AB.The first is based on the performance of the AB of its objective function - to protect electrical circuits against overcurrent with specified characteristics, the second - on the price / quality ratio of the selected type of AB.
There are two main criteria for choosing AB.The first is based on the performance of the AB of its objective function - to protect electrical circuits against overcurrent with specified characteristics, the second - on the price / quality ratio of the selected type of AB.
The rated current AB is selected with a value less than or equal to the maximum current for which the protected circuit is designed. If the electric circuit is made of a copper wire with a conductive core cross section of 1.5 mm2, to protect such a circuit, choose AB with a rated current of not more than 16 A. Since for wires of this type, the maximum allowable working current should be no more than 21 A, and the allowable current short circuit duration of 1 s should be no more than 170 A, the protective characteristic AB can be selected C type. In this case, the current limitation class can be any, but it should be borne in mind that the sooner the circuit is disconnected during a short circuit, the less likely it is to have an emergency and the more chances are to keep the electrical equipment in good condition.
The number of AB poles is selected based on the number of protected electrical circuits. For a single-phase circuit, two-pole circuits are usually used, for three-phase circuits, three and four-pole ABs.
Among foreign manufacturers should be noted: ABB, Legrand, Schneider Electric, General Electric, Siemens, etc. Among domestic manufacturers can distinguish products KEAZ, IEK, Contactor, etc. To solve budget problems, the products of a Russian company are fully justified. To implement business ideas, you can use more expensive and high-quality products of foreign manufacturers ABB, Legrand, Schneider Electric.
For practical reasons, it is advisable to build a system of protection against current overloads according to a two-level scheme. The first level of protection is based on VD. Since consumers of electricity are usually distributed in separate rooms, it is advisable to carry out the second stage of protection of a distributed type, grouping the electrical circuits according to their functional purpose and supplying each group with a separate AV, which will avoid a general power outage in the event of a local current overload. In this case, the VD should be designed for the total current of all consumers of electricity.