Earth plays an important role in electrical wiring. It ensures the safety of a person from electric shock in case of short circuit and other emergency situations. Grounding must be in accordance with the modern requirements of the PUE (electrical installation rules). When carrying out repairs, it may be necessary to disconnect the working grounding bus, so you have to install portable grounding. In order to do everything correctly and safely, you need to understand in what sequence it is necessary to carry out the installation of portable grounding. To do this, use the recommendations and installation rules.
What is portable grounding?
All types of grounding have the same purpose and belong to protective equipment. The portable type is used on temporary objects in which it is impossible to designate a permanent connection to the ground.
The temporary grounding kit includes flexible wires with clamps at the ends of permanent fixation. Typically, conductors are connected in three lines when connected to three-phase installations. Tips should have insulated rods, since work can be carried out at voltages above 1000 V. This ensures safety in case the bus is under voltage. There are also models for single-phase equipment. They have one conductor with a clamp on the end.
The use of portable grounding is dangerous without protective equipment in the form of automatic machines and fuses. This is due to the fact that a short circuit may cause a fire in the power cable.
Grounding portable equipment performs another important task - protection against induced voltage. When the installation is de-energized, induced currents from adjacent conductors may form on the cable. It is the earth that prevents the appearance of such currents, so the installation of grounding for electrical equipment is required.
equipment requirements
Work with any electrical equipment requires safety precautions. The main requirements are:
- Cable integrity over its entire length. It should be without kinks, cracks, violation of the structure itself, turns and breaks of wires. Otherwise, such a wire is prohibited to use.
- Do not use insulated cables. Under the protective sheath, it is difficult to control the integrity of the current-carrying core.
- The cable should have the same cross section over its entire length. The choice of area depends on the load to which it is connected. The calculation can be carried out according to special tables. With insufficient cross-section, the device will not withstand the load and, accordingly, will not protect a person.
- The length must be selected so that the grounding bus and equipment can be connected without tensioning the wire. It should not be suspended except when grounding points are located at a height. This applies to power lines.
- The conductor is selected so that it can withstand the appropriate climatic conditions of use. It must not heat up and must withstand the dynamic tensile load.
- The insulating hoses must be so long that the clamps overlap without getting close to or touching the operator.
- We recommend using screw-tightened clamps to ensure a secure fit. The material must be resistant to heat and form a scale at the junction.When tightened, contact should not deteriorate.
- The clamp and conductor are connected by welding or crimping. It is also possible to establish a connection with a nut to a soldered contact point. It is forbidden to use only overlay and soldering, since such a connection is destroyed under the influence of elevated temperatures.
- When installing for a long period, you need to check the equipment at regular intervals.
The described rules began to be presented by the PUE. Their observance is mandatory at work. The safety, health and life of people directly depends on this.
Installation algorithm
Grounding is carried out by live conductors, where voltage is supplied from. Between the connection point and the place where you need to conduct the earth, there should not be converting elements with galvanic isolation, which include voltage multipliers, stabilizers and transformers.
An operator who sets up and installs temporary equipment must be in protective work clothing. This is a transparent face mask, mittens, insulating boots, a dielectric foot mat. Work without protection is prohibited.
All work is carried out in the strictly given sequence:
- Attaching a common or central clamp to the ground bus. It must be valid and verified.
- Using a tester or indicator screwdriver, the absence of voltage on the current-carrying conductor is checked.
- Visual inspection of the structure and all conductors.
- Control touch with a clamp of a current-carrying core.
- Reliable fixation of the conductor.
- Next, a design test is performed.
Work must be carried out by at least two specialists. This allows in case of electric shock to shut off the power supply, provide first aid to the victim and call a doctor. Only professionals with high qualifications and sufficient work experience should be engaged in installation and connection.
The protection method also depends on the load. In the case of connecting to equipment with voltages above 1000 V, a special rod of dielectric material is used. If the voltage is less, enough work with dielectric gloves.
Ground removal
The procedure for removing grounding is as follows:
- Checking for lack of voltage in grounded areas. It is carried out by testers and indicators.
- Disconnecting the clamps from the electrical installation.
- Disconnect the clamp from the ground bus.
Before applying the load to the unit again, remove the portable earthing switch from the operating area. It is also necessary to check the regular grounding, to which the equipment is connected, in the junction box for operability. A working ground must be installed, otherwise it is forbidden to use the installation.
What to do in the absence of regular grounding
In the case of operation on an ungrounded installation, a temporary ground loop is made. It is a triangle, made in accordance with all the rules of the organization of protective earth. After that, portable grounding equipment should be connected to it. A substitute is made of metal pins, profiles. Be sure to take care of the device in advance with which the product will be pulled out of the ground after the completion of repair work.
Instead of such a circuit, you can make another installation in the form of an earthing switch with a reverse hammer. Using this design, you can easily install the rod into the ground and pull it out.
When installing grounding on a temporary circuit, you must adhere to the same rules and recommendations that are given for a stationary grounding bus.
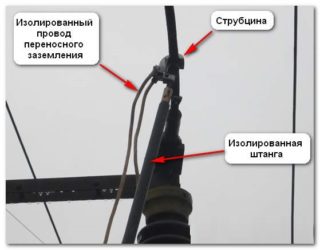
Pole grounding
The grounding temporary construction for power transmission lines differs from ground-based options using long rods. Also, at the ends of the conductors, gripping hooks will be placed instead of clamps. There is no regular grounding when working in the field, therefore, a portable design for a specified period is also used. Usually the necessary kit is included.
The absence of screw clamps leads to a weaker and less reliable contact with the current-carrying core. For this reason, you should make 2-3 redundant grounding for each high-voltage conductor.
Grounding is done from the ground. The operator is on the ground, installation from a pole is prohibited.
Power lines are connected by single-phase rod earthing switches. Between themselves, the conductors are connected to the ground at the point of intersection with the ground electrode.