High-quality preparation of liquid for drinking or domestic needs is the key to good health. There are various methods of water purification. The simplest one is filtering. However, special coagulating reagents for water treatment and water treatment are often used. Chemicals should be used strictly for their intended purpose in exact dosages.
Purpose and scope of coagulants for water treatment
Coagulation is a chemical process, as a result of which dispersed, colloidal impurities become larger in the processed medium. They turn into flakes visible to the human eye, which are formed in the process of adhesion of small particles. Later flakes precipitate and are removed using mechanical filters.
Coagulation as a method of water purification is used in the following areas:
- VOC (for clarification of drains);
- industrial dirty water treatment;
- pool cleaning;
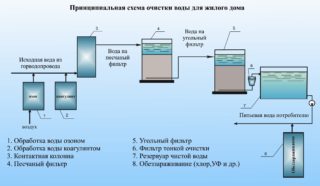
- preparation of drinking water.
Processing of the liquid medium with coagulants for its further use requires preliminary accurate analysis. As well as a meticulous calculation of the dose of coagulant during water treatment.
Types and principle of action of drugs
 The mechanism of work of reagents is a special chemical process. Any coagulating drug at the molecular level has a positive charge, while all impurities in a liquid medium are negative. In this situation, all dirt molecules are unable to combine into larger formations precisely because of the negativity of their molecules. For the human eye, impurities are not visible at all. Sewage looks just cloudy. The reagent added to the water dilutes the negative charges of the impurity atoms and, as a result, large flakes form. The liquid becomes visually cleaner, lighter, there are no smells in it.
The mechanism of work of reagents is a special chemical process. Any coagulating drug at the molecular level has a positive charge, while all impurities in a liquid medium are negative. In this situation, all dirt molecules are unable to combine into larger formations precisely because of the negativity of their molecules. For the human eye, impurities are not visible at all. Sewage looks just cloudy. The reagent added to the water dilutes the negative charges of the impurity atoms and, as a result, large flakes form. The liquid becomes visually cleaner, lighter, there are no smells in it.
All coagulants are based on chlorides, sulfates or polyoxysulfates of metals such as magnesium, iron, titanium or aluminum.
There are two types of chemicals reagents for water treatment:
- inorganic;
- organic.
 The first (inorganic) are titanium dioxide or iron / aluminum sulfate. Each of them has a number of features:
The first (inorganic) are titanium dioxide or iron / aluminum sulfate. Each of them has a number of features:
- Titanium dioxide. The most expensive of all types of coagulants. At the same time, it purifies the liquid to a drinking state. Titanium dioxide removes dirt and bacteria from water. Doses of the drug are used less than when working with other agents. At the same time, the settling time of the medium treated with titanium dioxide is reduced by several times, in contrast to the work with other inorganic reagents.
- Sulphate of aluminum. The product is easy to use, does not require long settling after dilution. But the reagent is sensitive to the pH level of water. It is desirable that the indicators do not go beyond 6.5-7.5. Otherwise, aluminum sulfate will be ineffective. In addition, this coagulant seriously affects the level of acid-base balance of the liquid. After processing, it must be brought back to normal.
- Ferrous sulfate. Helps purify water from oily impurities, hydrogen sulfide, reduce the concentration of heavy metals in it.
Iron sulfate in the medium is not completely dissolved.
All organic reagents are produced solely on the basis of hydrochloride (it is also called aluminum polyoxychloride). Such coagulants for wastewater treatment have a number of advantages over inorganic preparations:
- quick dissolution of the product in water;
- high quality liquid cleaning;
- economical consumption of drugs;
- high coagulation rate;
- reduced settling period;
- low residual percentage of aluminum and salts in the treated medium after the chemical process;
- the ability to use hydrochlorides even at low street temperatures, in cold liquid environments.
If an organic preparation enters the soil, it does not change the acid-base balance of the soil, and does not form an environmental disaster in the region.
Criterias of choice
Coagulants are selected by the following parameters:
- Form of the drug (liquid or powder). The first option is more convenient, since the reagent is already ready for use. But solutions, as a rule, are more expensive than dry preparations.
- Type of product (organic / inorganic). It is selected depending on the problem with which the struggle is being waged. For the treatment of drinking water, it is better to take organics. Sometimes the user prefers the more expensive Aquaflow electronic installation. With its help, it is possible to form impurities in the processed liquid into flakes without adding reagents to the water.
When buying a drug, you should pay attention to the integrity of the package and the timing of the manufacture of the product. If the coagulant is expired, most likely it will not give the expected effect. It will also be useful to pay attention to the GOST marking and composition of the product. In their absence, it is better to refuse the purchase.
Application features
 Before using inorganic preparations, you should take care of a respirator and at least mittens. They will help protect the skin and mucous membranes of the respiratory tract from irritation if particles of the reagent get into the latter.
Before using inorganic preparations, you should take care of a respirator and at least mittens. They will help protect the skin and mucous membranes of the respiratory tract from irritation if particles of the reagent get into the latter.
Otherwise, when using the coagulation method, you must adhere to such rules:
- Before pouring the drug into a liquid medium, it is worth disconnecting the filter system. Otherwise, the flakes will simply clog the installation.
- It is necessary to calculate the displacement of the tank to determine the exact dose of the drug. The volume is calculated by the width, length and depth of the pool. All measurements are made in meters. If the bowl is round, measure the depth and diameter. The finished value is already converted to liters.
- With severe contamination of the fluid, 1.3 of the recommended dose of the drug can be used. That is, to slightly increase the effect.
- The dry reagent must first be diluted in water in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations.
- For temporary reservoirs, it is better to build special mounted skimmer-mounted intakes. They will collect the resulting flakes. You can also use a special vacuum cleaner.
- As a rule, after 9-12 hours, all flakes precipitate. You can also remove them from the bottom with a water vacuum cleaner.
A properly cleaned liquid is suitable for further use without the need for replacement. This is extremely important for large artificial reservoirs (pools, aquariums, fish ponds), so coagulants are popular as a method of cleaning liquids.



