What is power consumption?
When deciding when buying about how much power an air conditioner consumes, many users confuse different concepts. It should distinguish between:
- power consumption, that is, energy consumption from the mains;
- cooling / heating power (cold and heat output), that is, the amount of cold / heat generated after the processing of the used electrical energy.
Both of these values are measured in watts (watts) or kW (kilowatts). On any air conditioner and in the instructions for it there is information about how much energy it can consume, and also give out after, but already in the form of heat or cold.
Do not confuse these designations with W / h and kW / h, since these designation units convey the amount of energy already generated per hour. For example, an air conditioner with a power consumption of 700 watts worked for one hour, while it needed 700 watts-hours or 0.7 kilowatt-hours.
Typically, the power consumption indicated by the manufacturer may differ significantly from the actual. This is due to the fact that the nominal value in the manual is calculated according to the measurement standard ISO 5151, where the temperature values are strictly fixed - with closed windows and doorways 27 ° C indoors and 35 ° C outside, and the operating time per day does not exceed 2 hours. When operating climate control equipment in domestic or industrial conditions, these parameters vary greatly.
Energy Efficiency and its Connection with Power Consumption
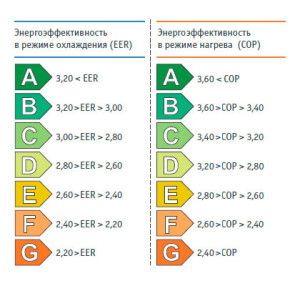
There is such a thing as energy efficiency of an air conditioner. What it is? This definition means the ratio of the power output for cold / heat and power consumption, indicated in EER (cooling) / COP (heating) - energy efficiency coefficient. The larger the final figure, the higher the efficiency, and the less costly in terms of electricity costs the climate device is considered.
It should be remembered that any air conditioner consumes 3 times less energy than it produces, since electricity is used only for the circulation of freon through the refrigeration circuit and its conversion.
How efficient the power consumption of the air conditioner can be can be considered with a concrete example. If we assume that at moderate temperatures the household wall split system has an average electric power consumption of about 1.2 kW and produces a cold load of about 3.5 kW, then its energy efficiency coefficient will be closer to 3 kW. This is considered an average performance.
Regarding the EER and COP values, they created energy efficiency classes consisting of 7 units (A-G), as shown in the picture. The most favorable in terms of electricity costs are considered devices that comply with class A.
What determines the power consumption
What generally determines the power consumption of the air conditioner when using? Several factors are important here:
- compressor potential;
- temperature difference in the street and indoors;
- function to be performed;
- cooling power, i.e. cold load.
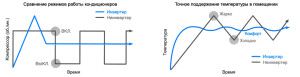
Although it is worth noting immediately that on these reasons, the dependence of the consumption of the air conditioner occurs only in inverters. Models operating in start-stop mode (temperature reached → turned off; temperature changed again → turned on) have constant values of electricity consumption, but require more time to reach the set parameters.
Compressor capacity
The lower the compressor speed, the lower the energy consumption.Such energy-efficient air conditioners most often have an inverter way to control the operation of the compressor, when the saving mode of energy consumption is automatically switched on when the set temperature values are reached.
That is why inverters are considered a more profitable acquisition in comparison with conventional start-stops, which always work in the same power mode.
Temperature difference
The greater the temperature difference between the room and the street, the greater will be the power consumption of the air conditioner in kW. If the street is 40 ° C, and at home you need to set 22 ° C, then the costs will be greater than at 25 ° C outside.
In an air conditioner with linear energy conversion, the power consumption per hour will not change, but when the set temperature is reached, its compressor will turn off and turn on when it increases.
Miscellaneous Functions
Different functions require different time consuming. In principle, there is an analogy with the previous paragraph. There will be no changes in the power consumption of the air conditioner in kW per hour, but with large time costs, the number of kW that the air conditioner “ate” will increase, therefore, the cost of paying for utility bills will be higher.
Cold work
How is the relationship between cooling capacity and how much power is consumed by the air conditioner from the network? In fact, the relationship is simple - the higher the cold load indicators, the higher the electricity consumption.
How much do household and industrial air conditioners consume
The difference between how many kilowatts air conditioners for domestic and industrial use can consume is very large. Household models serving an area of up to 25 m² often take less than 1 kW with the rest of the average performance. Typically, air conditioners installed in apartments do not exceed consumption of 2.4 kW or 2400 watts. They have a single phase connection. For semi-industrial devices (channel, column, cassette) and especially industrial (chillers, server cabinets and the like), electricity consumption can reach hundreds of kW. As a rule, they have a three-phase connection.
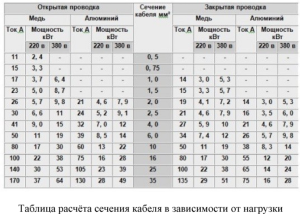
Most often, it is not necessary to bring a separate power cable to household refrigeration devices, and you can plug them into a regular outlet. For the rest, it is necessary to lay a separate wire with a large cross section.
Also pay attention to which outlet is given for power. Old Soviet sockets may not pull a load of more than 1 kW.
Calculation of electricity consumption
Before acquiring a refrigerator, many are interested in how to determine how much energy an air conditioner consumes per hour / month or other period of time.
It is impossible to calculate exactly these indicators for 100%, since it is simply unrealistic to know in advance the temperature at which the device will be used, the frequency of its inclusion and many other parameters. But, starting from the consumption of the air conditioner per hour (indicated by the manufacturer), you can approximately calculate the daily rate of expenditure.
If we assume that the start-stopper will work 6 hours a day with moderate heat in the summer, and the indicated demand is 800 watts, then it will spend 4.8 kW per day. With an average cost per kWh of 4.32 rubles, the cooling price in one day will be about 21 rubles. Then it’s easy to approximately calculate how much electricity the air conditioner consumes per month - just the resulting value is multiplied by the number of days per month. For example, 30 days for 21 rubles will cost an extra 630 rubles plus the waste of electricity.
Again, it should be borne in mind that these indicators are very arbitrary. In extreme heat or cold, data can change significantly.Someone will need round-the-clock operation of the device (top floor, a house with a flat roof, the sunny side), therefore, how much electricity is consumed per month will increase by 4 times, that is, 630 × 4 = 2520 rubles.
According to manufacturers, the energy consumption of an inverter air conditioner is reduced by an average of 40%. If we assume that the power values of the inverter split are the same, then under the conditions described above, the consumption will not be 0.8 kW, but about 0.5 kW. Here, the daily expense will be 13 rubles when working for 6 hours, and the monthly waste of only 390 rubles. If you work in 24/7 mode, the amount will be slightly more than one and a half thousand.
But all the calculations here are relative, since even for several hours the air conditioner cannot function with constant potential, especially since this cannot happen with round-the-clock operation. In inverter models, even the rated power consumption of an air conditioner per hour is constantly changing.
How much energy is required, it will become more or less clear after the first month of operation for cold in hot weather or for heating at extremely low outdoor temperatures. Then the user will be able to set the required number of working hours of the device to create a comfortable temperature and calculate the cost of paying for electricity bills.