Modern air conditioning systems (multi or split), with the positive qualities with which they are characterized, there are still a number of drawbacks in this equipment. The most important minus is the length of interblock communications is insignificant (no more than 25 m). Even with this length, a reduction in the power of the installation cannot be avoided, the loss coefficient is at least 30%. Another significant drawback is the number of indoor units; they have to be installed up to 4 units per elite apartment or cottage, and this does not affect the architecture of the building in the best way.
 Until now, the way out of this situation was the installation of one channel split system with the distribution of the cold air flow not in the only direction, but according to the system design, that is, along several air ducts. These systems are mounted behind the false ceilings of offices or residential apartments. In addition to reducing the height of the ceiling (at least 20 cm due to the diameter of the thermally insulated duct).
Until now, the way out of this situation was the installation of one channel split system with the distribution of the cold air flow not in the only direction, but according to the system design, that is, along several air ducts. These systems are mounted behind the false ceilings of offices or residential apartments. In addition to reducing the height of the ceiling (at least 20 cm due to the diameter of the thermally insulated duct).
This technical solution has another significant drawback - the regulation of airflow cooling with uniform indicators for all rooms at once, because one indoor module did not allow coordinating the specific temperature in each individual room. A way out of this situation was found. In 1982, the world's first multizone VRV system was developed and launched on the HVAC market. The manufacturer of this equipment has become a brand Daikin.
Specifications and features of VRV air conditioning
In fact, multi-zone VRF / VRV air conditioning systems are an improved version of typical split systems:
- as in classic air conditioning systems, several indoor modules can be connected to one unit installed outside the room at once, but in VRV / VRF their number can be several tens at the same time;
- as for the power of VRV / VRF modules, then, as in traditional ones, it can be 2-25 kW, by type they are cassette, wall, channel and so on.
In addition to the similarities listed above, multi-zone air conditioning air conditioning systems have at their disposal a number of distinctive characteristics, in comparison with traditional climate equipment:
- In the usual version, you need to lay a freon pipeline between the external module and each internal one, in VRV or VRF you do not need to do this, here all mounted modules are connected to a common duct, which consists of several pipelines. This highway consists of 2 or more copper pipes, about 30 internal modules-blocks and about 3 external ones can be connected to it. This will speed up, facilitate, reduce the cost of the installation process.
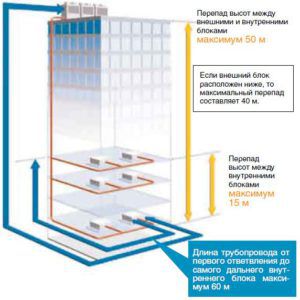
- The maximum distance of the duct from the external to the internal module is 100 meters. The height threshold (vertical) between the blocks is 50 meters, which makes it possible to mount an outdoor unit in multi-zone VRV / VRF in almost any zone: in the basement of the building, on the roof and a few tens of meters from the building.
- You can control this air conditioning system through a remote control, from a computer where specialized software is installed, or from a centralized control panel.
- Unlike a conventional split system, the internal VRV / VRF blocks, the temperature set by the program, are held with the highest accuracy, the percentage of error is ± 0.5 degrees Celsius.
Thanks to such positive data, one such system is able to cover the need for residents of a multi-storey building in a favorable and comfortable microclimate. Today, it is practiced to install a capacitor unit outside the boundaries of the building, the length of the freon route allows this to be done.
VRV / VRF conditioning: difference and similarity
VRV - literal translation - "variable refrigerant volume." VRF is also considered an abbreviation with the same decoding. Just with the release, at the end of the past century, the first VRF air conditioning system, this abbreviation was patented by the Daikin trademark. Other manufacturers of such equipment are simply forced to use a different VRF name, which, in fact, does not change the essence of the matter. Both VRV and VRF condenser units have a single freon line to which all evaporative devices are connected.
About the benefits of VRV / VRF conditioning
- Systems can significantly save electrical energy due to heat recovery by special modules. This refinement makes it possible to work the system for indoor cooling and heating. Daikin is a leader in terms of energy performance. True, the operation of such equipment with HRV is a winning option in any case, regardless of manufacturer;
- space saving. The indoor units are compact, the length of communications makes it possible to remove the external module to the maximum;
- systems work perfectly in all weather conditions, even in severe frost from -200С to -500С;
- variety in design decision. The length of the pipeline, flexibility, the ability to expand the system even after putting it into operation, replacing old equipment with new or out of order;
- low level of noise from the operation of the blocks;
- high rate of reliability. VRF / VRV complexes have an integrated self-diagnosis system, the function of auto recovery after sudden power outages;
- ease of installation.
Cost multi-zone system
High cost is the main and only minus of these systems. Cost has always been the main and important side in the choice. We give the estimated cost of VRF or VRV systems from leading brands.
| Total area (in m2) | Mitsubishi heavy ($ per m2) | Mitsubishi Electric ($ per m2) | Daikin ($ per m2) | Sanyo ($ per m2) | Cost Range ($ per m2) |
| ≥500 | from 170 | from 205 | from 250 | from 140 | from 140 to 250 |
| ≤500 to 1500 | from 160 | from 185 | from 220 | from 130 | from 130 to 220 |
The price is calculated for standard office premises with a useful area of less than 500 squares and more than 1,500, provided that for every 6 squares there is no more than 1 workplace. As for the residential premises (high-rise buildings), the cost of the systems is 30-50 percent lower due to the low heat gain of residents, household appliances.
Despite the simplicity of the design and installation of multizone systems, it is not recommended to do this on our own. The purchase, design and installation should be done exclusively by professionals.