Heating a house, organized with the help of a boiler, radiators and distributing pipes, is a complex engineering communication. Pressure in the heating system is a characteristic that directly affects the durability and proper functioning. Differences, a decrease or increase in the indicator lead to the destruction of structural elements, shutdown of heating, costly repair.
Types of pressure
When designing and installing heating, specialists are guided by many parameters, each of which is necessary for proper operation.
The pressure is necessary to move the heated coolant through the pipelines from the boiler to the radiators, and to raise the liquid to the upper floors of the building.
Allocate pressure and working pressure. Pressure testing is created at the initial installation, as well as annually during preventive work to prepare for the heating season. With increased indicators, the places of possible leakage of water from the pipes are determined, the identified malfunctions are eliminated. Under the worker understand such an indicator at which the system is in working condition throughout the cold season.
The performance indicator is summarized from the static and dynamic component. Static pressure creates a water column in the risers due to gravity. The higher the house, the higher the rate. The dynamic characteristic is determined by the operation of circulation pumps, which supply coolant to the upper floors, pump liquid through pipelines and heat exchangers (radiators).
What is considered the norm
The norm indicator differs depending on the number of storeys of buildings, heating design and functioning principles. The pressure in heating systems in apartment buildings reaches 6–7 Atm for the supply section of the pipeline. For return, a characteristic of 4–5 atm is characteristic. When pressure testing, the pressure should reach 10-12 Atm.
When replacing radiators, pay attention to the characteristics indicated in the product passports. The maximum value for batteries installed in multi-apartment buildings cannot be less than 12 Atm. Pipes were originally designed for such a pressure, and the weak point is the threaded connections through which leaks occur.
In private homes, a pressure of 1.5–2 Atm is sufficient to supply the coolant to the third floor. The same indicators are needed in individual heating schemes of apartment buildings.
In devices for heating a private house, copper tubes of boiler heat exchangers, which withstand 5–6 Atm, are more often subject to destruction.
What is the danger of swings
Low and high pressures lead to malfunctions of the entire heating system or breakdowns requiring expensive repairs.
At low rates, automation (for modern models) stops the flow of energy and the boiler turns off. If the heating stops for a long time in the frosty season, the pipes, radiators, boiler heat exchanger will be destroyed.
In addition, with a low rate, the pressure may not be enough to efficiently pump the coolant throughout the system. Without heat, the upper floors and radiators that are farthest from the riser pipes will remain.
An important indicator for the operation of a warm water floor. The maximum length of the circuit reaches 100–120 m, which creates resistance to the movement of the coolant. With insufficient pressure, the circuit will stop heating up.
With increased pressure, water begins to ooze through the threaded connections of pipes and radiators. Possible destruction of structural parts.
Low pressure reasons
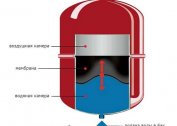
The pressure depends on the design features of the heating. In communications with natural circulation and leaky expansion tanks, the pressure depends only on the height of the water column. The cause of the fall may be a low water level.
In unpressurized systems, water evaporates from the surface of the reservoir or may leak through unpressurized connections. As the indicator decreases, water is added to the required level. Water evaporates gradually, so if the pressure drops sharply, you need to look for a leak.
In closed systems with hermetic expansion tanks, there are more reasons:
- not enough water / antifreeze;
- there is no pressure in the air cavity of the expansion tank or air leaks through the swap spool;
- rupture of the membrane;
- a gradual decrease in the internal cross-section of the pipes as rust, lime, and dirt deposits accumulate;
- malfunction of the circulation pump;
- air jams in highways and radiators.
After the system is initially filled with coolant, air remains in it. As it is vented through the bypass valves, the pressure will gradually decrease, adding fluid is required.
It is possible to reliably identify a problem only with an integrated approach and analysis of the circumstances in which the characteristic has decreased.
In multi-storey buildings, a decrease in the indicator occurs when the circulation pumps are turned off or the radiators or pipes are aired. To eliminate the last malfunction, they must install Mayevsky taps or automatic bleeders on the radiators.
In the case of boiling or overheating of water in the system, oxygen can be released from it. Gas is easily compressed, so pressure can drop.
Increased air emissions are observed when installing new aluminum radiators. At the first heating, there is a sharp release of air from the coolant, as a result of which the indicator decreases.
Why the pressure rises
The volume of any liquids increases with increasing temperature. For example, water when heated from 10 to 80 degrees will expand by 4%. If the internal volume of the pipeline and batteries is 100 liters, after heating it will have 104 liters. In antifreeze, the same indicator is close to 7%.
Water cannot be compressed at low atmospheric pressure. Excess coolant from a closed system cannot pour out, the pressure increases sharply.
To prevent increased pressure in the event of frequent changes in the temperature of the coolant (autumn and spring), as well as creating a reserve capacity for the liquid, the volume of the expansion tank is selected based on 10% of the capacity of radiators and pipelines.
Based on the above facts, after filling the heating water and heating the coolant to the operating temperature, the pressure will necessarily increase.
At the initial filling, the coolant is poured into the closed system only until the parameter necessary to start the boiler (1–1.3 Atm) is reached. Final topping up is done only after warming up.
Increased pressure is observed in areas from the boiler to the radiators if the pipeline is old. In this case, the internal passage of the pipe cannot pass the entire flow of the coolant - pressure differences occur between the flow and return.
Accident prevention
Excessive pressure can cause permanent damage. To protect communications in closed systems, security groups must be established.
The group includes:
- pressure gauge;
- automatic air vent;
- safety valve.
The manometer is used to visually monitor the pressure in the system.
When air is released from the coolant, an air vent is activated. It is designed in such a way that it allows only gases to pass through; water will not flow out of the pipes.
For individual houses, a safety valve is selected that is configured to operate at 3 Atm. With further increase, the coolant will pour out of the nozzle. Surplus through the hose gets into the sewer or can be collected in a special container. A similar valve is installed in modern gas and electric boilers.
The security group must be installed in systems with solid fuel boilers or non-volatile gas boilers.
When the power is cut off, the circulation pump stops working, while the fuel continues to burn. The coolant, remaining in the heat exchanger of the boiler, heats up, boils. The pressure rises to critical values, an explosion occurs with the destruction of boiler equipment.
The safety group is installed on the supply pipes when exiting the boiler, and not on the return line, which does not heat above 50-60 ° C.
Central heating pressure adjustment
In apartment buildings connected to central heating systems, water hammer often occurs. Particularly often, differences occur during technological work, during pressure testing, during the first start of heating with the advent of cold weather.
Radiators can be secured by installing a gearbox in front of the radiator. You can install it yourself between the control valve and the battery. Work is carried out after a seasonal shutdown of heating.
There is pressure in the pipes in the summer, it is created by a water column in the main line.
Choose a gearbox designed for 6–7 Atm. This figure is enough for radiators to work on any floor. All modern batteries easily withstand this pressure.
Often gearboxes are equipped with air vents, which simplifies the maintenance of the heating system.
Knowing the possible causes of pressure drops, a decrease or increase in the indicator, it is easy to find and eliminate the cause of the malfunction. Equipment manufacturers took care of the user, developed and produced devices for automatic regulation of important characteristics. Protective equipment can help prevent accidents, the elimination of which can be costly.