The correct selection of the heating system ensures the comfort of living in a private house, allows you to save on utility bills. Open and closed heat supply systems provide efficient heating, but differ in equipment, installation complexity and operation cycle.
Features of open and closed systems
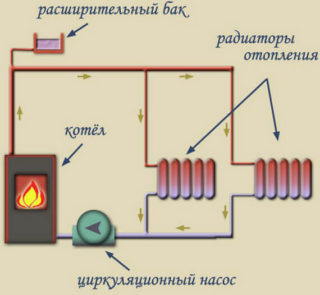
To warm the house, use a closed type of design of the movement of the coolant, including a boiler, radiators and pipes. The system works on the principle of heating water to a certain temperature in special equipment, moving along the pipeline to radiators and then transferring heat to warm the rooms. After cooling, the liquid returns back to the heating device, forming a repeating cycle.
Open system
To understand what an open heating system is, it is worth using the multi-apartment type of buildings as an example. This type of heating involves the use of a special storage tank, actively functioning in most multi-story buildings. On the roof of the high-rise building is an expanding tank to collect excess water. The tank is not tight, which allows the vapor to escape into the external environment.
The open version is mounted without a circulation pump. The coolant is routed through the pipes in a natural way. After heating in the boiler to a certain temperature, the pressure rises, and hot water, rising up, pushes the cold. The volume of water during heating also increases, so the excess goes into the expansion tank. The cooled coolant is directed back to the system.
Closed type of communications
A closed heat supply circuit provides a pump that provokes the movement of water through pipes. Forced circulation is also realized with the help of pipes, boiler, radiators, expansion tank. The metal tank is sealed, consists of two sealed parts, has the following content:
- internal rubber diaphragm - heat-resistant membrane;
- gas in small volume - factory nitrogen or air accumulated in the line.
The membrane divides the tank into two compartments - for collecting excess heated water and for arranging air.
The coolant moves through the system, but at the time of heating, the tank valve takes the excess. They enter the expansion tank, penetrate the membrane and are pushed back with gas. After cooling, the circulation pump pumps water back into the system, while simultaneously monitoring pressure readings. Thus, the deaeration of the heat carrier occurs.
The main differences
The difference between an open and a closed heating system is as follows:
- The location of the expansion tank. In the open - the top floor of a private house or the roof of a multi-story building. It is allowed to place the tank in a closed place anywhere.
- Insulation from air access. Unlike an open, a closed highway is protected from airflow. Additional pressure at the high points prevents airing of the batteries.
- The complexity of the arrangement. An open system will differ from a closed one in the type of pipeline. Large diameter products are mounted taking into account the location of the radiators, the air slope, the presence of rotation and rises.
- Organization costs. Closed heat and water supply requires financial costs for the purchase of thick-walled pipes. You can save on an open system using small-diameter trunk lines.
- Noise level.Forced type of circulation in a closed line involves the use of a pump. With proper installation, the equipment will not make noise.
Creating a closed house heating will save 10 to 40% of energy resources per year.
System Connection Options
 Laying of communications is carried out in a dependent and independent way. The first option is simple and low cost on components. The second method is used in new buildings.
Laying of communications is carried out in a dependent and independent way. The first option is simple and low cost on components. The second method is used in new buildings.
Dependent method
The specificity of the scheme is an intra-house thermal unit with an elevator. The heat point mixer mixes the hot water from the external line with the return. The coolant receives a temperature of up to 100 degrees. The benefits of dependent systems include:
- water supply for heating and supply directly from the heating main;
- simplicity and inexpensive price for input equipment for one subscriber;
- exposure to large temperature fluctuations;
- small diameter pipes;
- reduction of coolant flow.
Among the disadvantages of central heating are high water consumption, difficulties with temperature control and energy overruns.
The internal line is dependent on external heat supply.
Independent way
 The scheme provides for the presence of the main and additional circulation circuits that are separated by the heat exchanger. In the main circuit, water is supplied from the boiler room or CHP to the central heating unit, it is sent from it to the heat exchanger. An additional circuit will be home heating, which receives heat from the network.
The scheme provides for the presence of the main and additional circulation circuits that are separated by the heat exchanger. In the main circuit, water is supplied from the boiler room or CHP to the central heating unit, it is sent from it to the heat exchanger. An additional circuit will be home heating, which receives heat from the network.
The system works on the principle of heating water in two isolated circuits. The external heating mechanism works on a closed internal network without further mixing of the liquid. Among the advantages of an independent scheme:
- the ability to connect any number of heat exchangers;
- use of water for heating and household purposes;
- lack of pressure fluctuations in the home circuit;
- temperature control in rooms with a thermostat;
- the presence of drinking water in the domestic hot water supply;
- filtration of the heat carrier from salts in a small circuit.
Cons of communications - the need for periodic washing of the heat exchanger, the cost of the purchase of equipment and regulatory elements.
Pipe routing features
Depending on the location of the main pipe, battery connection technology, supply risers, wiring technology is selected.
Single pipe method
With single pipe wiring, a horizontal and vertical layout is used. Laying the pipes horizontally eliminates the adjustment of the amount of water, therefore bypasses are additionally used. The vertical location of the highway is typical for high-rise buildings.
Two-pipe method
The two-pipe reception of the wiring provides for the supply of two pipelines to one radiator - for supplying warm water and removing cold water. In an apartment or house, you can implement the following schemes:
- gravity - the circulation of warm water occurs naturally;
- classic - dead end system;
- ring - the coolant moves along the way;
- radiation - heat is supplied from the distribution manifold to radiators individually.
The two-pipe system is suitable for underfloor heating, where the heating circuits play the role of batteries, and pipes and the comb with mixer are mains.
Types of communications by type of circulation
In open and closed lines, the coolant can move in two ways.
Natural circulation
The system is organized without a pump, it works from the difference in fluid density during heating and cooling. The heat carrier is heated in the boiler, acquires a lower density and lightness, as a result of which it goes up. In a cold state, water moves along an outstanding riser - a pipe with a large diameter.By wiring and to heating devices, the coolant moves from top to bottom, cooling when heat is transferred.
In the cold state, the density of water rises, and it is sent to the heating tank. The pipeline runs at an angle. The system is distinguished by non-volatility - can be used in a private house or in the country. Among the minuses of natural circulation:
- complexity of installation due to pipes with a large diameter;
- unaesthetic appearance;
- the need for periodic topping up of the coolant;
- a small quadrature of the heated rooms.
The system uses an unpressurized open container.
Forced circulation
For communications, a circulation pump is used that activates the movement of water. The system is characterized by ease of arrangement, advanced features and a small pipe diameter. The user himself regulates the temperature or sets it in automatic mode. The disadvantage of forced circulation is its volatility.
Installation Rules
The rules for connecting equipment and creating a system depend on its type.
Open system installation requirements
When arranging should:
- Choose the lowest point for the heat source and the highest for the tank.
- Use pipes with a large diameter to move the coolant.
- A narrow pipeline is necessary to normalize the pressure.
- Install a tall riser that evenly distributes water.
- Exclude a large number of corners, forks and junctions.
- Mount the system in a confined space - up to 159 squares.
- In private households, it is better to put a good circulation circulation.
The open system is suitable for a small country house or cottage.
Installation procedure for a closed system
If you install a closed heating system with a pump and an expansion tank, you must:
- Put the boiler in the basement and the expansion tank in the attic.
- Provide high-quality thermal insulation of rooms with a capacity and riser.
- Do not use a large number of fittings.
- Do not overheat water.
- Drain the coolant if the system does not start in winter.
- Form a pipe slope of 2-3 mm per 1 m of the circuit.
The principles for calculating the cross-section and slope of the closed heating pipeline are prescribed in SNiP 2.04.01-85.
Self-organization of the heating system
A good and high-quality heating option can be done with your own hands, taking into account the costs of designing, purchasing equipment and the complexity of the organization. The best option for a private house is a closed type of communications with a circulation pump and tanks. Its creation is carried out as follows:
- Communication calculations. Ordered by the project company or made using the online calculator.
- Coordination of the project, obtaining permission and technical conditions.
- Purchase of equipment. You will need a heating boiler, pump, pipes, expansion tank, radiators (circuits, if a heated floor is planned), air vents, shut-off devices, automatic controllers.
- Boiler installation and boiler room equipment. High-quality ventilation is organized in the room, a chimney is arranged. Walls, floor and ceiling surfaces are sheathed with fireproof materials.
- Installation of the circulation pump, distribution manifold and metering devices.
- Connect piping to battery locations.
- Installation of radiators.
- Crimping system. The first launch is carried out in the presence of specialists.
The collector circuit is difficult to install and is expensive, but by adjusting the contours, the living conditions in the room will be comfortable.
There are several differences between open and closed heat supply communications. Choose a heating system depending on the conditions and installation location. An open highway is easy to organize on your own. Create a closed system should specialists.