The insulated Finnish foundation (UFF) is more in demand on the domestic market for the construction of low-rise buildings than the Swedish stove. There are many reasons for this, one of them is that it is more customary for a private developer to see buildings with a high base. At the same time, UVF contains some elements of the Swedish technology: a warmed base, which makes it possible to avoid unnecessary heat loss into the ground.
Features of the device of the insulated Finnish foundation

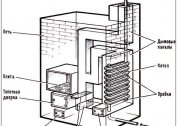
UVF is a foundation structure of the house, in which there is a strip foundation of a shallow type along its perimeter - it is realized in the form of a monolithic structure made of reinforced concrete or prefabricated from blocks based on a concrete heel. Inside there is a solid flooded plane. Elements are separated by a layer of thermal insulation and are independent of each other. Under the stove, a leveling bed is arranged, which is also isolated from the screed with extruded polystyrene foam or a similar type of insulation.
In addition, according to the technology of Finnish engineers, it is planned to equip the thermal barrier around the building, laying it under the blind area.
Pros and cons of engineering solutions
The positive qualities of Finnish development are reflected in the following points:
- Due to the ability to arrange a high base tape, there is no need to organize earthwork to deepen and level the soil base, especially on a pronounced relief.
- Screed with all utilities can be done after the construction of the box.
- The independence of the tape and the floor allows the dismantling and repair of the latter without the risk of disrupting the supporting structure.
Among the shortcomings in the first place is the complexity of the project and serious financial investments in it. UVF requires a certain professionalism and a high culture of construction work.
What is the difference from other technologies

If you compare with other methods, the technology of organizing UVF can only be compared with a Swedish insulated stove (UWB) similar in principle to construction. The main differences:
- In the Swedish version there is only a reinforced platform without a tape reinforced around the perimeter.
- The trough of pouring concrete for USP is an extruded polystyrene foam of a special shape with sides.
- In UVF, you can get a higher base, the tape in it is insulated on both sides around the entire perimeter.
- The Swedish technology has a solid reinforced frame, while the steel skeleton of the insulated Finnish monolith under the screed and in the tape is not interconnected.
In the financial sense, the arrangement of the UVF may cost more than the Swedish project, but the costs of building the first one can be extended in time.
The applicability of technology in practice
The technical parameters of the standard UVF make it possible to introduce this type of foundation in any climatic zones of the Russian Federation. If the weight indicators of the structure being erected are within the normal range (based on 3 tons per linear meter of shallow tape), the Finnish slab can be arranged on soils of any mechanical composition.
It is possible to increase UVF loads and erect stone masses up to 5 tons per meter instead of frame walls.To do this, you need to increase the supporting heel, and for each specific case, you need to calculate the width of the latter.
On average, any one-story houses with lightweight frame-type walls meet the norms of loads on the foundation foundation of the Finnish model.
Technological stages of the construction of the insulated Finnish stove
The foundation is one of the most critical building elements, so when it is built, certain operational steps are followed. The stove, developed by Finnish engineers, due to complexity, requires strict adherence to production technology:
- Ground marking and planning works.
- Organization of drainage system and waterproofing.
- Fill the tape base.
- Bookmark thermal insulation sheets.
- Adding soil under the stove.
- Installation of a barrier to moisture and the passage of heat under the floor.
- Pouring concrete screed base.
The last three stages from the list do not have to be performed primarily in the complex of all construction works of the building. You can drive out the walls, install the roof, and then, in a weatherproof room, prepare a pillow and fill the floor.
Land marking and earthwork
It is most convenient to mark the boundaries of the foundation of the strip foundation with stakes with twine stretched between them. Up to half a meter make a take-out beyond the border of the wall, where the perimeter of the blind area ends. Earth operations are reduced to removing soil (the remaining surface should be without inclusions of plant debris) from the trench under the device of the supporting heel of the tape and drainage.
Drainage and bedding
In the resulting trench (from the edge of the future concrete heel), a pipe wrapped in geotextile with small holes is laid so that there is a bias towards the discharge of storm water. All this is covered with a layer of gravel 20 centimeters high and slightly rammed. Geotextiles are also placed on top of the rubble.
Drainage when installing a shallow foundation should be given special attention, since otherwise the base can easily be washed away and the load-bearing structure will be destroyed.
Organization of a tape monolith
First of all, a concrete heel with a metal skeleton made of reinforcement inside is poured around the entire perimeter of the building. The width of this support should not be less than 0.6 meters, and the height - 0.3 meters.
Monolithic MZLF on top of the heel must be reinforced with 12 or 14 reinforcement. Therefore, inside the formwork set to the height of the base, the formwork is knitted from the rod frame. The resulting structure is poured with concrete and allowed to harden and stand.
To give the foundation a fortress, it is advisable to periodically water it from a watering can, especially on hot days.
Insulation and backfilling works inside
After removing the formwork, the inner part of the socle is insulated with polystyrene sheets (the polymer thickness should not be less than ten centimeters), fastening the latter with umbrella dowels. After that, the entire pit is covered with a geotextile, over which a gravel layer is poured, followed by a vibratory rammer.
Waterproofing device
A bituminous waterproofing is laid out on a gravel pillow, which is simultaneously welded together with a gas torch. There should be at least 3 layers of such a barrier. Also, this material is introduced into the base insulation. On top of this pie lay a polystyrene insulation ten to twenty centimeters thick.
Floor filling
The entire space under the future floor is reinforced with a grid (any cell can be selected, but no more than 15x15 cm) onto which the system floor pipe is installed. In addition, all communications should also be brought out: electricity, water and sewage. The screed is poured with concrete.
It is important to fill the floor at a time, avoiding breaks in time. To do this, it is convenient to use the services of trucks with concrete mixers.