Polyethylene foam or foamed polyethylene (hereinafter referred to as VPE) is a synthetic material that has low thermal conductivity, therefore it is used for insulation of floors, greenhouses, in the automotive industry and many other industries. It is called foamed because it has a porous structure. The material achieves such physical properties thanks to a special production technology.
Features of Foamed Polyethylene
To obtain a foamed insulation, the granules are poured into a melting tank and an additive is added, then the mixture is heated and blown out, where the material cools down. Then it is leveled and twisted into rolls. If it is necessary to impose VPE on the foil, do this by heating two materials, connecting them together.
This is just one technology, but there are others. Foam polyethylene chemically or physically, subjecting the raw material to pressure. Inside, air cavities are formed, closed from each other by partitions, due to which the VPE does not allow heat and sound to pass through well.
Material characteristics
Foamed polyethylene of various thicknesses is produced - from 1 to 200 mm. This material is light - its density is from 20 to 80 kg / cubic meter. Technical indicators are as follows:
- The temperature regime is from minus 60 to 100 degrees Celsius. It is impossible to operate over 100 degrees - VPE is a combustible material. When heated, it is able to melt, so it is used most often to protect against cold, for example, pipes are wrapped underground. At low temperatures, polyethylene foam does not change properties.
- This is a vapor-tight film, so it is not used where there is a risk of condensation.
- It absorbs water weakly: when completely immersed in a liquid, it is able to gain a maximum of 3.5% moisture within a month.
- It absorbs noise well. The greater the thickness of the VPE, the better the soundproofing properties.
- Chemically neutral, does not react with aggressive substances - alkalis or acids.
- In a biologically active environment is not exposed to fungus, bacteria. Rodents do not damage VPE during underground laying.
- Not toxic, even when burning does not emit harmful substances.
- Under favorable conditions, the material can last up to 80 years.
There is one significant drawback of this material: it is afraid of exposure to ultraviolet rays, so it must be additionally isolated from the sun with a film that does not transmit rays. Under the influence of ultraviolet light, it quickly disintegrates and completely loses useful properties.
Application area
10 mm of polyethylene foam can replace 50 mm of glass wool or 15 cm of masonry, so it is used in construction work to warm the outer walls. This reduces the overall cost of the facility.
In addition to the construction of VPE is used:
- For wrapping various items for safe transport. Air voids inside reduce the degree of mechanical stress.
- In the manufacture of upholstered furniture for the preservation of other materials prone to shedding.
- In light industry.
- For interior trim in the automotive industry.
- For the manufacture of sports equipment and equipment.
- Due to the strength of the material, it is used for the manufacture of prostheses, covering them with a metal frame.
The main scope is the insulation of various objects:
- roof, foundation, walls - internal or external;
- windows, doors, floor;
- ventilation or air conditioning system.
In addition, foamed sheet polyethylene is used as a gasket between fragile products during transportation, for example, double-glazed windows for window systems.
If you put foil foamed PE behind a heating radiator, more heat will remain in the room due to the reflective properties of the foil and low thermal conductivity of the material.
Types of Polyethylene
 At the moment, the industry produces a large number of polyethylene grades that differ in the production method and properties:
At the moment, the industry produces a large number of polyethylene grades that differ in the production method and properties:
- PE high pressure - LDPE;
- PE medium pressure - PSD;
- PE low pressure - PND;
- LPVD - linear high pressure, resistant to ultraviolet and aggressive substances, but less durable, so it is connected in layers.
- Low-pressure LPD has similar characteristics, but the material itself is durable, resistant to shock loads and compression. Similar technologies are used to produce household containers that can withstand low and medium pressure.
Linear brands of PE practically do not decompose in the environment, therefore packaging products are subject to special disposal in order not to violate the environment.
In addition to the above types, there are special materials that are used in construction. This is cross-linked and non-cross-linked polyethylene.
Stitched
Crosslinking is a technology that increases the strength characteristics of polyethylene, the formula of which is CH2. Molecules during a chemical reaction form a three-dimensional cellular network, since hydrogen leaves them, and carbon combines with each other. There is a concept - the degree of crosslinking. This is the ratio of "crosslinked" molecules and their total number.
There are three ways to sew PE:
- Physical. In the crosslinking process, the starting material is exposed to x-rays. The method is unreliable, since the products have an uneven degree of crosslinking due to poor penetration of the rays throughout the thickness. Also, PEX-C products are not able to return to their previous shape under deformations. At low temperatures, products crack.
- A chemical that is carried out using nitrogen (PEX-D grade) and silane (PEX-B) radicals. The method also did not receive distribution due to imperfection of products. The degree of crosslinking is 65%, which is very small.
- Peroxide Method (PEX-A). Hydrogen peroxide is used at high temperatures. Allows you to get the highest possible degree of crosslinking - 85%.
Products obtained by peroxide smelting are more expensive, but withstand heat up to 120 degrees. The tensile index also increases, cross-linked polyethylene pipes become more plastic, have a shape memory.
Ultra High Molecular Weight PE
Exceptional material for extreme conditions:
- high frost resistance;
- resistance to corrosion;
- resistance to abrasive action;
- low coefficient of friction;
- impact resistance;
- inertness to chemicals.
Ultra-high molecular weight PE is used for the manufacture of armored products, parts for mining and processing equipment, filters, pads for sports equipment. The basis is high-strength threads obtained at low pressure.
Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (HPS)
Additions of sulfur dioxide and chlorine make it possible to obtain rubber-like PE, which has enhanced heat-resistant properties, as well as resistance to external environmental influences. Used by:
- for the production of glue and sealants;
- for the production of wear-resistant floor coverings;
- in the manufacture of paints for concrete and metal.
The material is capable of dissolving in acetic acid and chlorinated hydrocarbon.
Foiled polyethylene and its properties
Reflective PE is used in the construction of underfloor heating, as well as for noise insulation of ventilation shafts, pipelines, expansion tanks. Material does not pass steam and water. It consists of two layers - foamed polyethylene and aluminum foil, sanded to a degree of reflection of 97%.
Advantages of foil PE:
- There is a certificate of complete material safety.
- It is not damaged by rodents, as it is inedible.
- Convenient for transportation.
- Fire safety. In domestic conditions it is impossible to reach high temperatures at which PE ignites.
- At the same time isolates heat and sound. At the same time, it is laid in a thin layer.
- A layer of 4 mm is able to replace mineral wool with a thickness of 8 cm.
To install foil polyethylene, there is no need to use a vapor-permeable film, since the material itself conducts water molecules well. Compared to mineral wool, it is worse, but condensate does not accumulate.
Of the disadvantages:
- PE with foil is very soft, therefore it is not used for plaster and wallpaper.
- Adhesive materials are used for wall mounting, since it is impossible to attach foil polyethylene in another way. The use of nails violates the thermal insulation properties.
For insulation of the external walls, PE with foil is used as additional protection against moisture and to reflect heat inside the walls.
There are several varieties of foil insulation:
- Marking A is PE coated on one side with aluminum foil.
- In - a covering from two parties. It is used for interfloor ceilings as a separate insulation.
- C - one side is foil-coated, the other is coated with adhesive for ease of installation.
- ALP - On one side is foil and laminated film, the other side is not coated.
- Marking M and R - corrugated PE coated on one side with foil.
Only polyethylene has heat-insulating properties. If it is used for laying under concrete, the aluminum layer does not fulfill its functions, since there is no radiant heat.
The use of foil PE in rooms with short-wave infrared heating of the floor may accumulate rays and burns on the skin and retina. This property does not apply to long-wave infrared heaters.
Insulation technology
Heat can go away in the following ways:
- through the floor;
- attic if it is unheated;
- cracks in windows or doors if they are old wooden;
- through walls if there are hidden cracks in them.
You can start to warm the room with internal walls in order to quickly heat an apartment or house.
To insulate the internal walls, it is better to use foil on one side of the VPE. It is possible to fasten on a wall self-adhesive rolled materials or use a construction stapler.
Work order:
- Spread the roll on the floor and cut the desired length along the height of the walls.
- Using a stepladder, attach the top edge of the material to the wall.
- Next, spreading the PE from top to bottom, attach it with small nails with wide hats or a stapler. It is important that the foamed insulation fits snugly against the wall.
The second piece of foamed polyethylene is applied end-to-end so that there are no empty spaces between the two sheets. After fixing all the joints are connected with aluminum tape to eliminate heat loss.
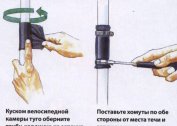
To insulate windows and entrance doors, you can use bundles of foamed polyethylene, which are sold in different diameters depending on the width of the slots. The material may have an adhesive surface on one side, so the place is first treated with alcohol to degrease, then PE is attached.According to its characteristics, the new material is better than traditional foam rubber, which turns yellow over time and crumbles under the influence of heat.
For laying under the screed to use foil material Penofol is not recommended for the following reasons:
- PE is thin and easily crumpled under the weight of concrete, so the thermal conductivity characteristics are reduced to a minimum.
- After a month of operation, nothing remains of the foil, in addition, it does not work in the absence of IR radiation under a layer of concrete.
- Floating thin screed, which does not adhere to the base due to the PE layer, begins to crack due to shrinkage, and with it tile.
For laying under a concrete screed, a special multifoil with a large mesh size that does not deform under the weight of concrete is used.
How can I glue together
In the process of laying foamed polyethylene, it may be necessary to adhere sheets to each other or to another material. Can be used:
- For the connection of VPE - Acrol contact, Quick-Bond, Neoprene 2136, 88 NP.
- To stick the foam to another material or to glue the foam sheets together - Akvalit SK-106P, Polimin P-20, Super Master, Ceresite or Anserglob.
- To connect the VPE with the wall, it must be cleaned, treated with an antiseptic, dried, then use Nairit-1, Porolon-2, 88 Lux or 88-Metal glue.
Before starting work, you need to think through your actions and provide what adhesives may be needed in the process.
Major brands
Penofol is the most popular material that you can buy at a construction supermarket. It is sold in rolls of 15-30 m, a width of 60 cm and a thickness of 3-4 mm. Penofol qualitatively interconnects layers by hot soldering - foil and foamed polyethylene, so there are no problems with operation.
Quick Step is a domestic company that bought a license from a European manufacturer and produces heaters made of foamed polyethylene, including pipes of different diameters.
Jermaflex
It produces PE of various grades, assuming different temperature effects during operation. You can choose the material with the best performance for a long service life.
Vilaterm
Brand Vilaterm produces bundles of foam of various diameters, which are used for insulation of windows and doors. The company does not produce rolled sheet varieties.