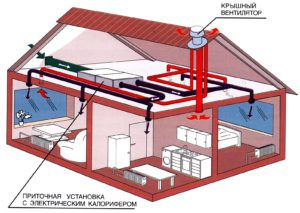
The main factor affecting the performance of a ventilation system is its proper design. For the system to function properly, it is necessary to make clear calculations of the area of the ducts. A correctly performed calculation of the ducts is responsible for:
- noise level;
- amount of electricity consumed;
- system tightness;
- unobstructed passage of air at the required speed and in the right volumes.
You can simplify the calculation process using specialized programs (calculators) or by contacting one of the relevant companies. For an independent search for the necessary parameters, there are calculation formulas, which, however, will be incomprehensible to a person without proper education. The calculation formulas are most in demand for any engineering work related to the design of ventilation systems.
To perform calculations using formulas, you must enter the required values instead of letters and perform the calculation. The accuracy of the final result depends solely on the clarity of the initial parameters obtained during the measurement.
Finding the right values
 Initially, to calculate the area, you need to get the information:
Initially, to calculate the area, you need to get the information:
- the smallest requirements for air flow;
- about the highest air flow rate.
- From the correct measurements and calculations depends:
- level of vibration and airborne noise, the limit of which depends on the accuracy of calculations;
- air velocity, which can cause both increased energy consumption and increased pressure;
- level of tightness - only with proper calculations the ventilation system will be tight.
During the design of the ventilation system, it is extremely important to pay attention to all sorts of aspects, as with this approach the system will turn out to be practical and no less durable. In addition, only properly designed ventilation can cope with its original tasks without any problems. It is especially important to pay attention to calculations when installing a ventilation system in large industrial and public buildings.
The air flow rate depends on the value of the cross-section of the area - the larger it is, the faster the air moves. Also, the value of this value will greatly reduce the level of energy consumption and aerodynamic noise of the system. Due to the large size of the cross-section, the total cost of the ventilation system increases. In addition, such ventilation cannot be installed in rooms with a false ceiling. You can solve the problem using rectangular ducts, but sacrificing, at the same time, the significant operational advantages of round products.
Ultimately, only user preferences determine which system is best to choose. If you need the greatest energy savings and the complete absence of aerodynamic noise, a square ventilation system is ideal. However, such ventilation takes up a lot of space. If the priority is only ease of installation or it is not possible to install a bulky rectangular system in a room, you should pay attention to products with a circular cross section.
With due attention to the design process, an ideal ventilation system can easily be achieved.
Formula Calculations
When performing the calculations, one must be guided by the formula intended for these purposes:
Sc = L * 2.778 / V,
Here Sc is the cross-sectional area; L - air consumption (m2 / h); V is the air velocity at a specific location in the structure (m / s); 2.778 - fixed ratio.
After all the required calculations, the result will be the number in square centimeters.
To find out the real ventilation area, use the appropriate formulas:
- round products - S = Pi * D squared / 400;
- rectangular products - S = A * B / 100.
Legend, here S is the area; D is the diameter; A and B are duct sizes.
Only at the end of all calculations and rechecking the result, you can begin real installation work. By this time, the entire project of the ventilation system should be completed.
Pressure loss
While in the duct of the ventilation system, the air experiences some resistance. In order to overcome it, the system must have an appropriate pressure level. It is generally accepted that air pressure is measured in its own units - Pa.
All necessary calculations are carried out using a specialized formula:
P = R * L + Ei * V2 * Y / 2,
Here P is the pressure; R - partial changes in pressure level; L - total dimensions of the entire duct (length); Ei - coefficient of all kinds of losses (summarized); V is the air velocity in the network; Y is the density of air flow.
He will get acquainted with all sorts of conventions found in the formulas, possibly with the help of special literature (reference books). At the same time, the value of Ei is unique in each individual case due to the dependence on a certain type of ventilation.
Other all kinds of help can be obtained on specialized forums on the Internet. However, the opinion of each specialist is unique in his own way.
Heater power
To determine the most suitable power of the heating device, it is necessary to consider:
- values of the required temperature;
- indicator of the minimum possible temperature outside the room.
It is accepted by experts that the minimum temperature level inside ventilation systems does not exceed 18 degrees Celsius. Internal temperature conditions depend solely on the external climate. For ordinary apartments, a heater with a power of 1–5 kW is most suitable. Public (including office) premises require a more efficient device, whose power is 5–50 kW.
To make the most accurate calculations of the required heater power, you can use the following formula:
P = T * L * Cv / 1000,
Here P is the power of the heater (kW); T is the difference in basic temperatures (indoors and out); L - efficiency of the ventilation system; Cv - heat capacity (0.336 W * h / square meters / degree Celsius).
Having made the necessary calculations, it is possible to choose a suitable air heater that fully meets the user's preferences. In addition, the accuracy of the results will affect the subsequent operation of the ventilation system.
Shaped products
 To calculate the necessary parameters of both shaped products and ventilation itself, there is no need to use formulas on your own. To simplify the entire design process, engineers created specialized programs (calculators) that are capable of calculating themselves. The only thing required of the user is to enter the requested values.
To calculate the necessary parameters of both shaped products and ventilation itself, there is no need to use formulas on your own. To simplify the entire design process, engineers created specialized programs (calculators) that are capable of calculating themselves. The only thing required of the user is to enter the requested values.
Only an engineer can calculate the value for fittings fittings independently. However, even professionals are not able to do without special tables, values and formulas with the necessary coefficients. A person without sufficient knowledge in the relevant fields is not able to independently carry out design.
When calculating the diameter of the duct, it is necessary to use a table of equivalent diameters. This table takes into account ducts with a large cross-section, where a decrease in friction pressure is equivalent to a reduced pressure of rectangular structures. Equivalent diameters are only necessary if you need to count rectangular facades using tables for structures with a large cross-section (round).
In both cases, a professional approach to computing is needed. If any parameters do not correspond to reality, the ventilation system cannot be installed.
It is possible to recognize the equivalent (equivalent) value in one of three ways:
- air consumption;
- by air flow rate;
- along the cross section of the duct.
Each of these values is fully associated with any parameter of the ventilation system. To determine each parameter, you will need to use an individual calculation table. As a final result, the value of the friction pressure loss is obtained. If all measurements were correct, regardless of the calculation method, the result will be completely identical. Errors in the calculation can occur due to violation of the requirements for measurements.
Additionally
More detailed information about the design (tables, formulas, reference books, etc.) can be easily found on the Internet at various thematic forums. The final result (the strength of both the structure itself and its fastenings) is completely dependent on correctly selected measuring instruments. It is easiest to make the required measurements using special calculators and other engineering programs. In this case, you do not need to perform the calculations yourself - you just need to enter the requested numbers.
In the case of online calculators, the result will be more accurate than with manual calculations. This is due to the fact that the program itself, in automatic mode, seeks to round the result to a more accurate and understandable value.
Round and rectangular ducts require a different approach to design due to different levels of complexity. Thus, when designing a ventilation system with a large cross section, the engineer will need to perform a larger number of calculations than in the case of rectangular products.
To independently calculate the parameters of shaped products from an engineer, you will need to actively use a variety of formulas with already selected coefficients.