Exhaust ventilation removes exhaust air from rooms in which there are sources of pollution. The complete set and characteristics of the exhaust installation vary depending on the purpose of the facility. Exhaust ventilation systems successfully operate in production, warehouses, kitchens and smoking rooms. Read more about how to calculate exhaust ventilation, about the types and principles of its operation.
General exchange and local
One of the defining parameters for exhaust ventilation systems is the scope. On this basis, local and general exhaust ventilation are distinguished.
General Exhaust Ventilation covers with its action the volume of all rooms in the building. An example is the familiar exhaust ventilation in apartments. Exhaust grilles are located in the upper part of the kitchen and bathroom, through them exhaust air must be drawn from the entire apartment. General exhaust ventilation is effectively used in housing, storage, sports and recreation facilities, in shops and shopping centers. That is, where the concentration of harmful substances in the air is low and they are uniformly dissolved throughout the volume of the room.
The general exchange type of exhaust ventilation is equipped when:
- hazardous substances penetrate into the air of the room, because machines and mechanisms cannot be sealed;
- there are no specific emission points for hazardous substances;
- local hoods can not cope.
General exchange exhaust ventilation reduces the content of hazardous impurities in the air of the entire room to the maximum permissible concentrations.
Local or local exhaust ventilation system necessary where harmful or hazardous substances are released into the air pointwise. It provides normal conditions for workers right at their workplace. Exhaust pipes are brought in here, which collect dust, hot air, smoke, toxic fumes and carry them out, preventing them from spreading. A good example of a local exhaust ventilation system is mechanical hoods in kitchens. The equipment of a local exhaust ventilation system is much cheaper than general exchange, and the amount of air removed is less. And this means the equipment is more economical. But if the pollution is dispersed in the air, the local exhaust ventilation system is ineffective.
Natural and forced
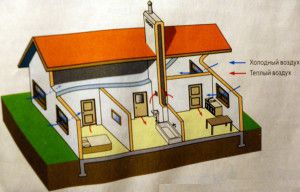
The principle of operation of any exhaust ventilation system is to evacuate the exhaust air. For its implementation, various methods are used. Exhaust ventilation system can be natural or forced. When the movement of air masses occurs according to the laws of nature, ventilation is called natural. In mechanical exhaust ventilation, air moves only through equipment. Mechanical ventilation is fully automated, the volume of exhaust and inflow are known in advance and comply with design standards.
Advantages and disadvantages of natural ventilation
The main advantage of natural exhaust ventilation in the apartment is low cost. Arranging it does not require serious costs, and the operation is completely free, no equipment for air exchange is required. The second advantage - accessories for exhaust ventilation do not take up much space.
A serious drawback of this type of exhaust ventilation is the unpredictability and uncontrollability of its work. The movement of air occurs due to the difference in air at the ends of the exhaust pipes.Therefore, under certain conditions, traction may not be.
When the house is colder than on the street, exhaust ventilation can turn into a supply air, drawing air into the apartment from the outside. For this reason, natural ventilation is installed in residential premises and less often in industrial ones.
In production, where a guaranteed outflow of air is required, this principle of operation of exhaust ventilation is not effective enough and can even be dangerous.
Exhaust ventilation calculation
The calculation of exhaust and supply ventilation of industrial premises begins with the identification of sources of toxic or explosive emissions. Next, the flow rate of supply and exhaust air sufficient to ensure sanitary standards is calculated. If there are no sources of harmful substances in the room, the calculation of exhaust ventilation is limited by the formula:
O=m * n,
here: ABOUT - air volume regulated by sanitary standards; m - fresh air consumption per worker per hour; n - the number of employees.
Value m SNiP is determined for each employee:
- in the presence of ventilators m = 30 cubic meters per hour;
- without air flow m = 60 cubic meters per hour.
If harmful or hazardous substances are released during the production process, the quantity and the need for fresh air to breathe are taken into account in the calculations.
Often, harmful substances are released throughout the workshop and it is necessary to reduce their concentration to maximum permissible concentration at the location of people, and then remove it using mechanical exhaust ventilation. MPC standards can be found in the specialized literature, for each harmful substance there is a threshold. We calculate the amount of fresh air needed to dilute to the MPC:
O = Mw \ (Co-Kn),
here: Mv - the weight of the harmful substance entering the air in 1 hour; To - specific concentration of harmful substances in the room air; Kn - concentration of the harmful substance in the inflow. Knowing the required amount of air, you can choose the engine power for exhaust ventilation.
If several harmful substances are emitted in the workshop, calculations are performed for each of them separately and then summed up. To determine the overall air balance of the room, the costs of all local exhaust ventilation for soldering and the total inflow are added up.
To determine the amount of supply air, we calculate the excess heat:
W = Ol + [3.6q - c * Ol (Tr - Tp) / c (T1-Tp)],
here: Ol - the volume of air removed by local extracts; q - the amount of heat generated by machines and products; c - heat capacity, taken from the directory, equal to 1.2; Tr - temperature of air removed from the working area; Tp - inflow temperature; T1 - temperature of air removed from the entire room.
Natural type
Consider how to calculate natural type exhaust ventilation. With this type of air exchange, the exhaust air is drawn through the shafts. It is replaced by fresh air from the street through specially equipped or spontaneously occurring gaps.
We calculate the pressure difference at the ends of the exhaust duct in Pascals:
∆H=g*L(Ωh-Ωb),
here: g - 9.8 - acceleration of gravity, L - duct length Ωh - air density in the street, Ωb - air density in the duct.
During aeration, the amount of air penetrates into the room, determined by the formula:
O=3,6*Q/(tv–tp),
here: 3,6 - specific heat Q - total heat gain, tv - blowing temperature tp - inflow temperature.
For the longest duct, a pressure loss is calculated equal to the total pressure loss of all segments.
In one section, the pressure loss is calculated as follows:
P=r*L + z,
here r - loss of pressure on the segment, L - the length of the duct section, z - losses from resistance.
Equipment for local exhaust ventilation
Shelters for completing exhaust ventilation are divided into three categories:
- located outside the source of pollution;
- completely overlapping the source of excretion;
- pereduvki.
A very effective method of localizing harmful secretions using shelters covering the source. But the technological process does not always allow the use of such a principle of exhaust ventilation. Other exhaust local ventilation devices:
- fume hoods;
- suction
- exhaust umbrellas;
- suction on-board, shaped and display types;
- removal of secretions directly from machine cavities;
- encapsulation (the machine is installed in a capsule).
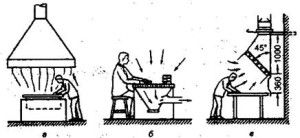
Suction must draw out harmful impurities with the lowest air consumption. Suction is often used in production, for example, as local exhaust ventilation for soldering. An important condition: accessories for exhaust ventilation should provide access to machines, without interfering with the work of employees.
Exhaust hood - The most common example of suction. Umbrellas are installed to collect hazardous impurities rising up, for example, as local exhaust ventilation of soldering tables. Exhaust hoods can work on forced or natural traction.
Pull out drobe removes harmful substances in the best way, creating a minimum air exchange. Cabinets are:
- with an upper suction to collect moist and hot air;
- with lower and combined suction to collect heavy vapors and gases;
- with side suction and snail fan for dust collection.
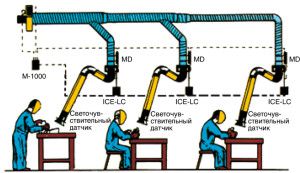
The engine and fan for exhaust ventilation create a swirl of air, preventing dust from spreading around the room. An example is the exhaust ventilation at a welding station. To weld small parts at the posts, exhaust ventilation cabinets with a top suction and a sliding shelter are equipped.
When working with non-toxic substances, the air velocity at the inlet to the device should be:
- 0.6 - 0.7 m / s,
- up to 1.1-1.5 m / s for the suction of toxic impurities (including vapors of heavy metals).
Suction panels it is advisable to use when dust, toxic gases and heat are released into the air. The panel is placed so that the flow of toxic substances passes as far as possible from the employee’s face and is connected to the exhaust ventilation motor with air ducts. The panels are installed, for example, as exhaust ventilation of welding posts where they work with large products. Double or single suction panels are hung at a distance of not more than 3.5 m from the welding site. For a suction panel, the air velocity should be:
- when working with hot dust 3.6 - 4.5 m / s;
- when working with toxic, dust-free discharge - 2.1 - 3.5 m / s.
Each square meter of the panel should draw 3300 cubic meters of air per hour.
Side suction used in cases where the object of the allocation of hazards is held by vertical lifts, that is, the space above it cannot be occupied. For example, in galvanic shops, harmful substances spread over the surface of a solution poured into a bath and are gradually sucked into the suction slot. On-board exhausts are air ducts with narrow inlets with a diameter of up to 100 mm, located at the edges of the bathtub.
Calculation of parameters of local exhaust devices
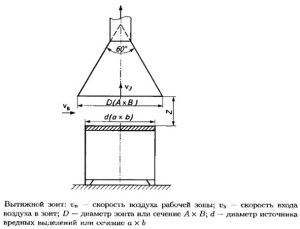
For the absorption of hazards directly in the place of their discharge at the factory most often install suction in the form of umbrellas. If the equipment supplier does not supply umbrellas, they are made according to the drawing:
Before calculating an umbrella for exhaust ventilation, it is necessary to determine:
- diameter (d) or dimensions of the emission area (a x b);
- air suction rate into the umbrella (Vz);
- air velocity in the working area (Vc);
- umbrella mounting height above the pollution source (Z).
A very important indicator determining the effectiveness of the pollution intake is the height of the umbrella.Therefore, it is advisable to hang it as low as possible.
We calculate the dimensions of the umbrella:
A=0,8*Z+a, B=0,8*Z+borD=0,8*Z+d,
So that stagnation zones are not formed at the edges of the catching device, the opening angle should be less than 60 degrees. In very low rooms it is allowed to increase the opening angle to 90 degrees. The height of the lower edge of the umbrella should be no more than 180 cm above the floor. If the air velocity in the room is more than 0.4 m / s, the umbrella is equipped with hinged curtains, which cuts off the contaminated air flow from three sides. The above calculations will help you pre-select the equipment, determine the price. But in order to calculate the exhaust ventilation in detail, you need to contact a specialist.
Do-it-yourself exhaust ventilation
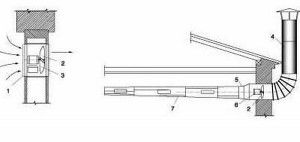
The easiest way to equip exhaust ventilation with your own hands in a private house. From each ventilated room we stretch the exhaust duct strictly vertically. Turns and bends reduce traction. Any protrusions, irregularities and changes in the diameter of the ventilation pipe also adversely affect air speed. The canal ends above the roof of the house. The cross section of the exhaust duct must be at least 100 square meters. cm, it is desirable to calculate it more accurately. Round exhaust ducts are more effective, since they create less resistance to air (the shorter the perimeter length, the less resistance).
If you equip the exhaust ventilation of the house with your own hands at the stage of its construction, you can hide the mines in the walls. Otherwise, you will have to additionally drill the floors, stretch the pipes or attach a brick box for the mine.
The mine exit above the roof is made out by hand with an exhaust ventilation umbrella, which covers the hole from precipitation and litter. Instead of an umbrella, it is advisable to install a deflector. It costs a little more, but enhances traction in the mine.
Mechanical exhaust system
Exhaust ventilation systems are produced by domestic and foreign companies: WentMashine, Alfa Vent. So, WentMashine produces exhaust ventilation systems from European components.
| Number of fan speeds | 4 |
| Performance | 260-700 cubic meters per hour |
| Input noise | 28-39 decibels |
| Fan power | 0.195 kW |
| Dimensions, cm | 52.8x45.7x28.8 |
| Weight | 16.3 kg |
| Installation location | Outside \ inside |
Table 1. Characteristics of the exhaust unit BW-700
The cost of exhaust ventilation systems from the manufacturer is 33-129 thousand rubles, depending on the power. In apartments and country houses, exhaust ventilation units are not practical. After all, it is necessary to simultaneously ensure a full flow of air from the street. Household supply valves and window vents cannot cope with this task.
Mechanical exhaust ventilation with a powerful engine and duct system is acceptable for commercial, public and industrial premises, where in combination with a supply unit it creates a complete air exchange.
Video on how to equip workshop exhaust ventilation with your own hands: