The issue of improving energy efficiency must be considered in the design and overhaul of private residential buildings. The forced-air and exhaust installation in the ventilation system is one of the effective solutions for saving on the payment of energy resources.
Types of ventilation systems
Changing the air in residential and utility rooms, in the kitchen and in the bathroom is a prerequisite for maintaining a healthy microclimate.
Ventilation is natural and forced.
In the first case, clean air flows from outside and is removed into the atmosphere due to the physical processes of traction in a high pipe.
In winter, cold air enters the house through windows, doors, supply ducts, and leaves the premises heated to room temperature - so up to 15% of energy is wasted on street heating.
Forced circulating systems use fans installed in the air supply or exhaust ducts.
In supply and exhaust ventilation, both processes are forced.
The principle of operation of systems with recovery
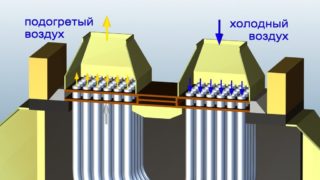
Ventilation with recovery works according to a simple scheme:
- In a place convenient for installation and maintenance, a recuperator is installed - a heat exchanger, to which a supply and exhaust ventilation ducts are connected.
- Warm room air from the room heats the cold coming from the outside.
- Heated clean air masses are pumped into the house.
- The process is then repeated.
It was experimentally verified that at a temperature of exhaust air of 23 ° C and incoming from the outside -20 ° C, in the best samples of recuperators, the incoming flows are heated to 18 ° C. In this way, energy savings are achieved.
Cold and polluted air in the recuperator do not mix - clean air enters the building from the street.
To increase the efficiency in different operating conditions, a wide variety of models of recuperators has been developed.
Design features
The classification of heat exchangers is carried out according to various criteria:
- technical specifications;
- method of placement;
- case material and internal elements;
- principle of action;
- design of work items;
- the physical environment used for heat transfer;
- automation and control scheme.
The choice is made after a thorough analysis of all the features.
Hardware Installation Location
When choosing the installation location of the main unit of the recuperator, consider where the fans or pumps are installed. The noise generated by the device can be a big hindrance.
Recuperators do not mount over bedrooms and nurseries.
By the method of installation, floor and hanging devices are distinguished, the surface affects the choice. If there are no solid capital walls, it is better to stay on the model installed on the floor.
Hanging devices can be hidden behind a suspended ceiling, but such solutions are suitable for industrial buildings. The vibration created by the fan and the housing is transmitted and amplified by building structures.
The heat exchanger housing can be horizontal and vertical. This does not affect the technical characteristics, but allows you to choose a model for convenient connection of air ducts.The fewer angles and turns, the less noise from air flows and less energy wasted on the movement of air masses by fans.
Typical construction schemes
All recuperators are conventionally divided into models of direct heat transfer and devices with an intermediate coolant.
The first class includes heat exchangers:
- chamber;
- rotary;
- lamellar crossflow and counterflow;
- tubular.
In devices with an intermediate heat carrier, freon or a water-glycol liquid is used.
Chamber
The device consists of two isolated cameras. The flows are automatically controlled by a movable damper.
At the first stage, warm air is sent to chamber No. 1, while the walls are heated. After a time determined by the automation, the damper changes the air flow - the street one goes to the heated chamber and heats up there, while the room one goes to chamber No. 2.
The process is cyclically repeated as the compartments are heated and cooled. The efficiency of devices does not exceed 50 - 60%.
Rotary
The heat exchanger in the supply and exhaust unit with a rotary type recuperator is the plate attached to the wheel. The shaft rotates slowly in the drum, the axis coincides with the flow of air. The drum is divided into two parts, one of which moves the air of the apartment, the other street. The impeller of the wheel, moving in the first segment, heats up. Further, by rotation, the heated blades move to another part of the drum, where they give off heat to the street air.
The control equipment allows you to turn off the heating mode in the warm season. The efficiency of the installation is about 80%.
The disadvantage of the model is the technical impossibility to completely separate the flows - about 5% of the air masses are mixed. The feature does not allow the use of devices of this type in rooms where SNiP are set to the maximum permissible values of pollution.
Lamellar
There are two types of models: countercurrent and cross-flow, the name depends on the direction of air movement.
Aluminum plates accumulate and give off heat, from which narrow guide channels are formed.
The manufacturing scheme allows mixing of air masses at a level of about 0.1%, which serves as the basis to consider the device airtight.
The efficiency of countercurrent recuperators depends on the geometric dimensions. Bulky equipment has a high cost and is rarely used for private homes.
In cross-flow heat exchangers, air flows cross the device perpendicularly.
Cross-counterflow heat exchangers are most effective for small dimensions. A large number of constituent elements reduces mechanical strength, therefore, such units are used only with small pressure drops.
Tubular
Structurally made of one pipe of large diameter, inside of which there are many tubes of a smaller section.
Warm flows, passing through thin tubes, heats them. A stream of street air is heated from the walls, which enters the house through a blower fan.
Ventilation with freon recuperator
Freon recuperators belong to the class of devices with an intermediate coolant.
The basis of the work are two physical principles:
- a change in the aggregate state of freon during heating-cooling cycles - the coolant, cooling, goes into a liquid state and turns into a gas fraction when heated;
- the property of a gas to be higher than a liquid due to different specific gravity.
The design is a multitude of annular tubes filled with refrigerant freon.
Tubes pass through the channels of the ventilation unit, and the exhaust duct must always be lower than the supply air.Warm air heats the lower part of the tubes, freon boils and rises into the upper cavity, through which cold street air passes. In the upper chamber, the freon in the tube gives off heat, it itself cools, passes into the liquid fraction and falls down the tube.
The advantages of the freon system:
- lack of compressors for pumping coolant, which means high reliability of the device;
- the complete absence of mixing of clean and polluted air, which is achieved by compaction of the places where the tubes cross the walls of the chambers.
Channel recuperator with intermediate heat carrier
The device consists of two heat exchangers that can be carried over long distances.
The equipment is suitable for the reconstruction of ventilation systems, the design of which did not initially include the possibility of heat transfer.
Work algorithm:
- Air from the exhaust duct passes through a heat exchanger consisting of tubes through which ethylene glycol liquid circulates.
- The coolant is pumped through a circulation pump to the same radiator installed in the supply duct.
- The liquid gives off heat to the supply air passing through the radiator grill.
- The pumping process is continuous.
To regulate the degree of heat exchange between the conveying tubes installed valves. In principle, this is similar to the heat transfer control scheme of heating radiators.
With any scheme for constructing recuperators, condensation forms in the device. For its removal, a container must be provided for collection and ways of further disposal outside the house or into the sewage system.
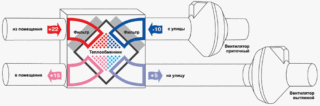
The main elements of ventilation systems
Ventilation with heat recovery in a private house does not only consist of a heat exchanger unit.
The system includes:
- protective grilles;
- air ducts;
- valves
- fans
- filters.
- automation and control bodies.
Lattices protect against accidental ingress of large objects, birds and rodents into the system, which can cause accidents. This option is possible when a foreign object gets on the fan impeller. The consequence may be:
- deformed blades and increased level of vibration (noise);
- jamming of the fan rotor and combustion of the motor windings;
- unpleasant odor from dead and decaying animals.
The total cross-section of the grill holes should not be much smaller than the cross-section of the air ducts, this leads to a decrease in the performance of the entire system.
Air ducts and fittings (turns, tees, adapters) are bought at the same time, trying to purchase products from the same manufacturer. The difference in size leads to gaps at the junctions, disruption of flow and turbulence.
Do not use corrugated ducts for ventilation with a recuperator, which create resistance to air flow and increased noise during operation.
Air valves are needed to temporarily change the parameters of air movement, for example, they can be used to block the inlet channel during a particularly frosty period of time when the recuperator cannot cope with heating the air to the required temperature.
Filters are installed in all ventilation models with recovery. They protect the equipment from street dust and tree fluff, which quickly clog heat exchangers.
Fans can be integrated into the recuperator unit or installed in ducts. When calculating, the necessary power of the device must be determined.
You can not save on buying fans - cheap low-quality products are not designed for long-term operation. As the wear and tear, the fans make noise, lead to vibrations of the ventilation components, which makes it uncomfortable to stay indoors.
Climate control
The recuperator is an integral part of the general system of supply and exhaust ventilation. The operation of the system cannot be configured once and does not change during the entire period of operation.
Modes change depending on the time of year, air temperature and wind strength, the desired climate parameters in the rooms.
The control systems include:
- Sensors of temperature, humidity, smoke installed in the premises and inside the equipment. By commands from the sensors, fans and other control equipment are turned on or off.
- Actuators and their actuators controlling the operation of valves, dampers, gate valves.
- Devices for controlling the operation of fans, pumps, rotational speed of rotor plates.
- Controllers of control devices that analyze the situation in the house, voltage regulators for stable and accurate operation of the equipment.
- Power backup units in case of a power outage.
The main functions of control systems:
- supply air temperature control taking into account microclimate parameters, external conditions, sensor readings;
- monitoring and changing the intensity of the temperature of the flows before and after the heat exchanger;
- air quality management, including CO2 content;
- heat exchanger frost protection;
- fan control;
- turning off the supply ventilation in the event of a fire and turning on the smoke exhaust system;
- monitoring the status and issuing information about the state of the filters.
Control panels are created individually, taking into account operating conditions, dimensions of the building and the requirements of property owners.
Selection rules
The main criterion for choosing an installation is its performance. It is very difficult to make calculations on your own, therefore it is better to contact specialists.
Parameters that are important when choosing:
- Coefficient of performance, which talks about how the temperature of the flows is redistributed, rather than saving heat. Real numbers are close to 65–80%. Statements about 90% and above are no more than marketing moves. About 15% of heat is lost through ventilation, so the figures for 50% energy savings cannot be true.
- Case material and thickness - thin metal devices are subject to vibrations and increased noise.
- Reliable information about the performance of fans, it must be selected with a margin of about 20%. At the maximum power indicated in the passports, the fan ceases to create the pressure necessary for air circulation.
- Composition and characteristics of automation systems, uptime during a power outage.
- Additional automation features for controlling air conditioning, humidifier, electric heater (if necessary).
A properly installed and configured ventilation unit with a recuperator will reduce energy bills by 10-15%. Waiting for more savings does not make sense. At the same time, comfort in a private house or apartment will increase markedly. Components of well-known companies work for a long time and without failure with the correct calculation and compliance with the installation rules.