The safe use of furnace and gas equipment is only possible with timely removal of combustion products and continuous air exchange inside the premises. This and some other functions are performed by chimneys of various types: from elegant decorations of country villas to giant monsters - indispensable attributes of industrial zones.
The principle of natural traction
The outflow of gas combustion products from boilers, columns and furnaces is made through ventilation and chimneys by means of natural draft. Traction is provided with a difference in temperature on the street and in the house. The higher the ventilation duct or chimney and the greater the temperature difference, the more intensively the chimney pulls. Therefore, natural ventilation works best on the first floors of multi-storey buildings and in the cold season.
The temperature of the combustion products above the working stove is about 200 degrees. The air temperature in the ventilation and chimneys is not more than 25 degrees and therefore the draft is very weak. In the summer, when the temperature in the street is higher than in the rooms, the draft can "tip over", that is, air is drawn into the apartments from the ventilation.
To a large extent, the effective operation of the system depends on the frequency of inspections of the smoke and ventilation ducts.
Reasons for reduced traction:
- contamination of the inner walls of the channels;
- roughness, narrowing of the walls;
- increase in the diameter of the channel;
- air leaks.
A significant part of the energy of the air moving through the channel is spent on friction against walls, when turning and reducing the diameter of the channel. The pressure loss indicator depends on the masonry of the smoke or ventilation duct, its length and condition. In the presence of protrusions, dust growths and roughness, the resistance increases. Therefore, timely inspection and cleaning of ventilation and smoke channels enhances traction.
In large diameter channels, even with perfect observance of the rules for the safe operation of chimneys and ventilation pipes, the draft is reduced, since the combustion products cool faster.
When air leaks in the channel, draft also drops, since the air temperature in the channel decreases, and its volume increases. Therefore, all hatches for pipe maintenance must be kept closed.
The draft in the chimneys during the operation of the boiler or furnace is about 14 Pa. In the ventilation ducts, it is much lower. Opening the vents in apartments, the direction and strength of the wind, and even the location of neighboring houses affects the draft. Ventilation pipes and chimneys should not be located in the area of wind backwater. This space is below the line leading from the highest point of the closest building to the horizon at an angle of 45 degrees.
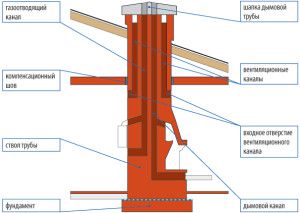
The design of ventilation pipes and chimneys
According to the rules of operation of chimneys and ventilation pipes, they are equipped inside the house to maintain the temperature of the exhaust air. You can arrange ventilation and smoke ducts from the outside, then they need insulation.
The laying of ventilation and smoke channels consists of clay bricks or heat-resistant concrete (asbestos cement). The thickness of the brickwork is from 12 cm, the concrete wall of the ventilation or smoke channel is more than 6 cm.The SNiP states that ventilation and smoke channels are arranged only vertically, without transitions and horizontal sections.
The device of the pocket (hole) for cleaning the chimney
Cleaning holes and a pocket 25 cm deep are left at the base of the chimney. The holes are covered with doors and faced with a brick mounted on a rib. Masonry is performed on a clay solution. In asbestos-cement pipes leave a leaf for cleaning.
A pocket is necessary so that when the masonry is destroyed, fragments of brick do not block the inlet, falling a little lower. In the pocket, all the garbage falling into the chimney also accumulates. If you do not provide a pocket, debris will gradually reduce the cross section of the chimney and impair traction.
Unsuitable materials for the installation of smoke and ventilation ducts:
- slag concrete;
- silicate, hole, slit brick;
- coarse-grained materials.
Although silicate brick resists high temperatures well, it is destroyed by carbon dioxide and wet fumes. If there are no other materials, SNiP requires a device in the ventilation and smoke channel of the inner cladding of red brick 13 cm thick.
Chimneys can be:
- mounted (from inserted asbestos-cement pipes);
- solid (made of brick).
Packed pipes are distinguished by smooth inner walls; they are supported by fireplaces or stoves with powerful (no thinner than 1/2 brick) walls. If the pipe is heavy, a reinforced concrete slab is installed on the furnace floor and the pipe is already attached to it.
Asbestos-cement pipe fittings are much lighter than brick pipes, they do not need to be disassembled during major repairs, they are quickly installed.
Brick chimney requires a special foundation, which is laid to a depth exceeding the depth of freezing of the soil.
When erecting low-rise buildings, prefabricated chimneys are used that are built into the wall or form a riser. Chimney walls are made of heat-resistant concrete.
In places where the chimney passes through the roof, leave a hole with a width of 13 cm or more. The connection between the chimney and the roof is covered by an apron made of stainless metal.
The chimney can have a slope of up to 30 degrees with an offset to the side of not more than 100 cm. Such segments should be of the same section equal to the section of vertical segments with smooth walls.
Brick chimney heads are covered with 20 cm plaster to protect against rainfall. Deflectors and umbrellas are not installed on chimneys.
Chimneys of gasified buildings
Ventilation and smoke channels of gasified rooms must rise above the flat roof by 50 cm or more. On a pitched roof 50 cm or more above the rib or to the height of the rib at a distance from the rib to the chimney of 1.5 - 3 meters.
The height of the chimneys of gasified rooms should be equal to the height of the exhaust ducts.
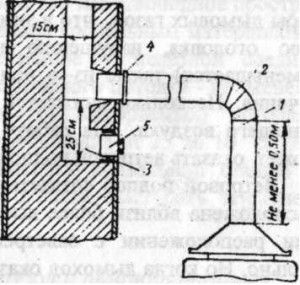
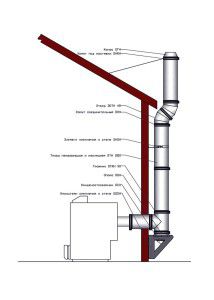
The heating equipment is connected to the system of ventilation and smoke channels in a gasified room through metal adapters. The length of the vertical adapter should be from 50 cm. If the height of the room is less than 2 m 70 cm and traction stabilization is used, the vertical adapter can be shortened to 25 cm. The total length of the horizontal adapters can be up to 3 m in new or up to 6 m in existing buildings.
The bias towards the boiler from 0.01 is allowed. Pipes must be fixed tightly with no chance of sagging. The pipe elbows are inserted into each other along the smoke path and overlap by 1/2 the diameter of the chimney.
The metal adapter is tightly attached to the chimney without protruding beyond the walls of the channel.
If the pipe is made of metal sheet, it is necessary to treat it with heat-resistant varnish.
The pipe is attached to the chimney, leaving a pocket of 25 cm and a hatch for control, as well as during the construction of the stove chimney.If the device is not equipped with a draft stabilizer, the construction of a damper with perforation of 15 mm through which the furnace is ventilated during idle time is required.
When converting old chimneys from furnaces for gas equipment, poor draft is often observed. The furnaces are heated for a longer time and the temperature of the combustion products is much higher than during the operation of a gas boiler, so the discharge of air from the combustion of gas is not enough.
Chimney Requirements
-
Structures adjacent to the chimney are protected by a layer of non-combustible material;
- From each furnace or gas heater during construction, its own ventilation or smoke channel is arranged;
- In already functioning buildings it is allowed to remove emissions from two furnaces or boilers into one chimney if they are located at a distance of more than 0.5 meters from each other;
- The laying of ventilation ducts or chimneys should be without ledges and withdrawals with the smoothest inner walls. Such masonry is done by specialists using buoys and squeezing with a wet rag;
- Brickwork is carried out on a lime-cement or lime-sand mixture. Seam thickness up to 1 cm;
- The pipe above the roof is laid out exclusively on a solution of cement;
- The outer walls of the chimneys in the attic are plastered and bleached;
- The main requirement for a chimney is its density;
- Between smoke and ventilation ducts there should be partitions with a thickness of 1 \ 2 bricks;
- The area of the internal diameter of the chimney should be equal to the area of the diameter of the outlet pipe of the heating device. In brickwork, the minimum section is 1 \ 2 bricks per 1 \ 2 bricks, and for the finished pipe at least 15 cm.
Chimney operation
Rules for the safe operation of chimneys and ventilation pipes require periodic cleaning and inspection. Without cleaning, a long-running chimney becomes a potential source of fire or poisoning of residents. The need to clean the ventilation and smoke ducts is determined by scheduled inspections.
A chimney made of brick or composed of asbestos-cement pipes after some time loses its appearance and works worse. On the inner walls, soot and soot accumulate, the lumen of the chimney is reduced, and draft is reduced. But there is another danger: combustion products can ignite. Substances released by soot destroy pipe material and masonry joints. The chimney tightness decreases, the fuel does not burn out completely, and the draft deteriorates.
Only periodic inspections of smoke and ventilation ducts will help to avoid dangerous situations.
If heating equipment is used every day, the inspection and cleaning of ventilation and smoke channels is 8 weeks. If the furnace is melted from case to case, you need to monitor the condition of the chimney twice a year: in the autumn before the start of the heating season and in the spring.
Chimney Check
Examination of smoke and ventilation ducts is carried out in the following cases:
- when converting stoves to gas fuel;
- when connecting to the chimneys of gas boilers;
- if necessary, diagnose the condition of the chimney and poor draft.
Purpose of checking ventilation and smoke channels:
- compliance of the masonry materials of the smoke or ventilation duct and the device with the requirements of SNiP;
- the presence of blockages;
- the presence of traction;
- the density of the walls of the chimney;
- the condition and presence of partitions separating adjacent building structures;
- the state of the head and its location relative to the roof, buildings and trees.
Checking ventilation and smoke ducts:
- To determine congestion in the chimney, a load in the form of a sphere, weighing 3 kg and up to 10 cm in size, is lowered into it from above. If the cargo passes unhindered, the channel is clear;
- To determine the isolation and density of the channels, the smoke method is used. In the window for cleaning, put a burning tow soaked in gasoline or a bundle of straw, burning a lot of smoke when burning. The chimney outlet is covered tightly from above. If the smell of smoke appears in nearby rooms or channels, then the walls of the channel are not dense;
- The purity of the walls of the channel is inspected by lowering an electric bulb up to 500 W with power into the chimney. At the same time, the density of the walls is determined. If there is light in the adjacent channels, then there are gaps.
Based on the results of checking the ventilation and smoke ducts, a cleaning is carried out. She may be:
- mechanical;
- chemical.
Mechanical cleaning is carried out with brushes and brushes made of metal wire. Under the weight of the cargo, they descend on cables to the chimney and scrape off all deposits from the walls. Some pipes (for example, ceramic) are difficult to clean - they may crack.
Dry cleaning is safer. In the furnace, a “log chimney sweep” is burned, which burns soot on the walls of the chimney. The material is impregnated with a chemical composition that decomposes soot and soot. But dry cleaning can not cope with thick deposits, so it is used as an auxiliary or preventive.
Experts recommend using dry alder or aspen firewood as a “chimney sweep”. They burn at very high temperatures and burn soot.
Industrial chimneys
The purpose of industrial chimneys and ventilation pipes is not only in the removal of combustion products, but also in maintaining combustion in the boiler units. In the recent past, most industrial chimneys and ventilation pipes were made of masonry. Today, it is being replaced more and more often with metal pipes with thermal insulation. The height of the structure can reach 60 meters.
According to the rules for the safe operation of chimneys and ventilation pipes, they need periodic cleaning. Prevention is carried out at the end of the heating season. And to exclude accidents, scheduled inspections of ventilation and smoke channels are assigned.
Design chimneys and ventilation pipes for the industry, taking into account each specific enterprise, since the task of construction is always unique.
When designing, environmental standards for smoke dispersion rates and maximum smoke concentrations are taken into account.
Types of industrial chimneys:
- Metal self-supporting. The cheapest are made of metal with thermal insulation. Very heavy. May be single-barreled or multi-barreled;
- Truss self-supporting. They are a farm column with insulated flues. 1 - 6 trunks are attached to one farm. The farm itself is made of rolled pipe;
- Metal columns. One powerful "shell" in which 1 - 5 trunks are hidden. Maximum height 60 m, diameter up to 3.5 meters;
- Stretch marks. A single-barrel metal pipe that is attached with braces. Most often installed in industrial enterprises. It is made by rolling. Such a pipe will last no more than 15 years, even if all the rules for the operation of ventilation and chimneys are observed;
- Front. The most economical option, does not need a foundation and supporting structure. It is attached to the facade, often this type of pipe is used in attached or built-in boiler houses.
The diameter of the pipes can be from 0.2 to 1.5 meters, and a height of 8 - 60 meters. There can be several gas outlet channels.
Depending on the conditions, industrial chimneys can be equipped with:
- air terminal;
- barrage lighting;
- stairs and service areas.
If a rectangular industrial chimney is installed, the correct aspect ratio is very important. The best is considered 1: 1.5 with sharpened internal corners.
The rules of operation of chimneys and ventilation pipes require their installation only on special self-supporting foundations.
And finally, a video on how to dismantle industrial chimneys: