Ventilation is a controlled exchange of air masses in a confined space. The control can be full or partial and is determined by the type of ventilation system. The quality of air exchange equally depends on the components, thorough assembly and compliance with sanitary-hygienic and technological standards for the operation of mechanisms.
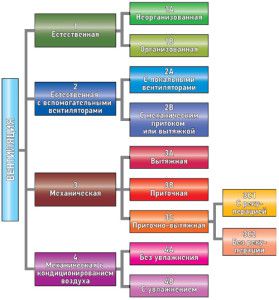
Types of ventilation systems
According to the current classification, all types of ventilation systems differ according to the following criteria:
- air flow principle: artificial and natural;
- nature of action: exhaust and supply, displacing and replacing;
- area coverage: to local and general exchange;
- device: on monoblock and modular.
The principle of movement of air flows
- In ventilation systems based on natural movement, flows are moved through differences in climatic indicators at different heights, inside and outside the building. These types of ventilation systems are equipped in multi-storey residential buildings. Clean air enters the rooms through the gaps in the building envelope. Waste is drawn through ventilation shafts and canals, the outputs of which are placed in toilets, bathrooms and kitchens. The validity period of a natural typical ventilation system is unlimited, its installation is cheap. Along with visible advantages, the scheme also has disadvantages. The aerodynamics of the natural ventilation system are directly related to climate performance. It is impossible to influence the traction, it may be completely absent.
- Mechanical traction used when guaranteed air exchange is needed. Such details of ventilation systems as air heater, filter, cooler, humidifier allow you to create the necessary microclimate indicators, regardless of the weather outside. Therefore, this type of ventilation system is universally used in modern buildings.
Nature of action
It removes exhaust air from public and industrial buildings, residential premises exhaust ventilation. And it delivers clean air, warming, cooling, filtering supply. Various configurations of the ventilation system provide many possibilities. When calculating the ventilation system, the supply and removal of air masses is always provided.
The most important task for designers is to properly balance the intensity of air intake and exhaust. In rooms for various purposes, the ratio of these values is different.
It also determines by what method the air will be cleaned in the room: by displacement or mixing. Combined ventilation is a type of ventilation system that uses a combination of mechanical and natural draft.
General exchange and local
Local ventilation serves the areas where the hazard is most intense. Such a scheme is good when you need to limit the area of distribution of steam or dust, not allowing them to fill the entire volume of the building. The most typical representative of local ventilation systems is a cooker hood. Its more powerful counterparts work everywhere in industry.
General ventilation fully covers the volume of the apartment, office, workshop. The simplest example in everyday life is an exhaust fan built into the ventilation grill of the toilet. The general exchange system can work on natural draft, but the local one cannot.
Monoblock or module
Monoblock installations include all the necessary accessories for the ventilation system, assembled together in a soundproof box. Monoblocks are made by supply, supply and exhaust, exhaust. To save resources, the supply and exhaust system is supplemented by a recuperator. This device uses the heat of the exhaust air to heat the supply air.
Advantages of monoblock ventilation units:
- all parts of the ventilation system are fitted to each other in the factory;
- monoblock is compact;
- the case is soundproofed, therefore it works quite quietly;
- you can pick it up yourself, using the manual for choosing ventilation systems;
- monoblock installation is much simpler than typesetting.
The type-setting installation is a constructor: a separate fan, filter, grilles, silencer, controller.
All details must be assembled on site, adapted to each other under a single ventilation system. The advantage of this installation is the ability to select the necessary parameters for any room. Minus - this should be done by a specialist, and the installation can be quite cumbersome.
| Mark | Producing country | Productive.
cubic meter \ h |
Price category | Dimensions |
| Arctos | Russia | 1000-2000 | Avg | 335x410x800 |
| Breezart | Russia | 350-16000 | Avg | 468x235x745 |
| Hummingbird | Russia | 500-1000 | Avg | 530x300x465 |
| Ventrex | B. Europe | 125-1200 | Avg | 320x320x1040 |
| Ostberg | Sweden | 185-785 | High | 225x319x760 |
| Pyrox \ sistemair | Sweden | 125-5000 | High | – |
| Wolter | Germany | 800-3700 | High | 335x410x600 |
Table 1. Supply units of leading manufacturers
Among the manufacturers of semi-industrial type ventilation systems in the Russian market, the leaders are: Remak (Czech Republic), Wolter (Germany), Ostberg, Kanalflakt, Sistemair (Sweden), Arktos (Russia). The listed companies represent typesetting and monoblock installations. As a rule, the cost of monoblock systems is 30-50% higher compared to typesetting of a similar class. Not so long ago, large companies began mass production of monoblock compact ventilation systems, approaching the price of modular ones. The price spread in the segment of monoblock models reaches 50%.
The most famous manufacturers of ventilation systems for special and industrial purposes: Vesa (Russia), Pirox (Sweden), Movin (Russia), Clivet (Italy), Arktos (Russia), Wesper (France). Due to the specific nature of industrial equipment, the selection of the ventilation system is carried out under the guidance of specialists from the supplier company.
Calculation of the main ventilation parameters
The main indicator required when calculating a ventilation system is air exchange or air capacity. To determine it, you need to know the purpose of all the rooms in the building and their area. According to the approved requirements, the air flow into the living quarters is:
- with openable windows - 30 cubic meters / hour;
- without openable windows - 60 cubic meters / hour.
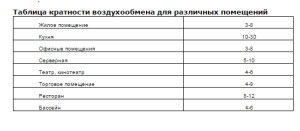
The air exchange is determined by the multiplicity and the number of constantly residing persons. The largest of the results obtained is used later.
After the ventilation system is calculated, we compare the results with the table data:
- apartments, premises from 100 to 500 cubic meters \ h;
- country houses - 500 - 1800 cubic meters \ h;
- public buildings and premises - 1 - 10 thousand cubic meters \ h.
Network calculation
Having learned the ventilation performance, you can design the network according to the following algorithm:
- we make the scheme of air ducts;
- we calculate the parameters of the cross section of the ducts, after which we determine the air flow;
- we select diffusers or gratings for the distribution of flows;
- we calculate airflow resistance - as an important indicator for the aerodynamics of the ventilation system.The longer the ducts and the more turns, the higher the resistance;
- we determine the power of the heating part and the voltage of the mains. For apartments, averaged values from 1 to 5 kW are accepted, for country houses and offices - up to 50 kW.
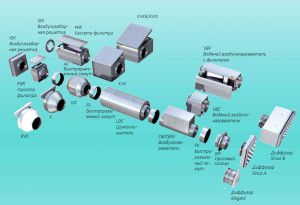
Ventilation components
Arranging a natural draft system requires very few investments:
- air ducts;
- intake and distribution devices.
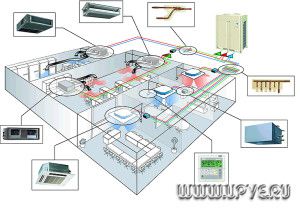
The mechanical type of ventilation system is assembled from the following components:
- Air intakes. This is the grille through which clean air enters the ducts. As a rule, additional lattices are covered with a grid. They are made of plastic or metal;
- Ducts. An air duct network is formed from the ducts. The air ducts are fastened together by adapters, tees. Round and rectangular sections are made of plastic, metal, foil. There are varying degrees of rigidity;
- Non-return valve. It is placed immediately in front of the air intake grille and closes when ventilation is mothballed. Prevents frost penetration into ventilation in winter. It can be electric or manually controlled;
- Heater. Available in water or electric. Water is used more widely in large industrial enterprises; for rooms up to 200 square meters, electric heating is more economical;
- Filter. Collects dust, settles down behind the backpressure valve. Depending on the filtering material (coal, non-woven fabric) there are fine or rough cleaning. Periodically, the filter must be cleaned or replaced, otherwise the load on the engine of the ventilation system increases;
- Fan. Must be included with the ventilation system. Selected by performance. In air exchange schemes, radial and axial fans are used. The design of the axial fan is such that air flows are parallel to the axis of the engine of the ventilation system. Radial or centrifugal more stable hold the speed of air movement in networks of complex configuration. The speed of the blades is regulated by step transformers or smooth converters;
- Silencer It is used to reduce aerodynamic noise in the ventilation system. It is installed at the outlet, sometimes additionally before the inlet. Effective silencers with a length of 100 centimeters;
- Throttle valve. Controls the distribution of air on the branches of the network;
- Distributors and adapters. Serve for distribution of air in the set directions;
- Automatic control system, including controllers for the ventilation system. The simplest ACSs dispatch air parameters and equipment operation. More sophisticated controllers for automating ventilation systems monitor the status of filters, are equipped with timers and are integrated into the control and safety system of the building.
When assembling ventilation systems, additional components are also used: recuperators, humidifiers, transfer grilles, coolers and dehumidifiers.
Ventilation assembly and commissioning
Installation of ventilation is preceded by preparatory work. Marks are made in the room: the placement of supports or suspensions for pipes, the branching points, the location of the main mechanisms. They assemble ventilation systems in high hangars and workshops from specially installed technological floorings or towers.
The sections of the ventilation system are collected at the bottom, after which they are lifted and fixed to the already installed highways. Oversized ducts with a diameter of more than 200 cm are connected by welding. Ventilation equipment is installed after fixing the ducts. Gradually during assembly, some components and components of the ventilation system are checked.Before commissioning and start-up, complex final tests of the ventilation system are assigned.
Commissioning works
Commissioning of the ventilation system is carried out in accordance with the "Rules for the production and acceptance of work" SNiP 111-28-75. Commissioning when commissioning the ventilation system consists in testing the parameters for compliance with the design values. When during the commissioning of the ventilation system it is not possible to achieve the necessary indicators, the causes are identified: violations during installation, malfunctions in the mechanisms, calculation errors. Prior to commissioning, tests are carried out and scheduling of the ventilation system and ACS is set up.
Commissioning objectives:
- identification of discrepancies in indicators of mechanisms and elements to design data;
- assessment of the quality of the materials used, installation work;
- leak detection joints;
- control of the coincidence of actual and design values of air flow;
- monitoring the compliance of the pressure and performance of the mechanisms stated in the passports;
- control of heating of heaters (this test of the ventilation system is carried out in the presence of a coolant in the pipes).
So, near the fans, the indicators may be close to the design, but behind the next bend of the duct the pressure and speed drop. Such defects are detected only during commissioning of the ventilation system.
Indicators measured during commissioning of the ventilation system:
- flow rate in ducts;
- flow rate on ventilation grilles;
- noise level;
- fan impeller rotation speed;
- pressure on the filters.
Commissioning of the ventilation system is carried out after the initial installation, overhaul or reinstallation.
| Operation | Price, rub |
| Specialist Departure | 2500 |
| 1 point measurement | 300 |
| Setting up 1 point to project indicators | 600 |
| System test | 4500 |
| Automated Control Setup | 7000 |
| Production of a ventilation passport | 1500 |
Table 2. The average cost of commissioning services.
Inspection and disinfection of ventilation
One of the conditions for the regular operation of the ventilation system is cleaning and, if necessary, disinfection. Deposits on the walls of the ducts violate the aerodynamics of the ventilation system and contribute to the development of pathogenic microbes.
The need for cleaning and disinfection is detected during the examination of the ventilation system. Control sanitary measures on ventilation systems are carried out according to the Methodological instructions of the Ministry of Health. Frequency of inspection of ventilation systems:
- 1 time in 36 months - in buildings with general exchange of natural and forced ventilation;
- 1 time in 12 months - in rooms with local supply and exhaust ventilation;
- 1 time in 4 weeks - in buildings with the release of hazardous substances of I and II classes.
Measures of sanitary-hygienic control of ventilation systems include research:
- concentration of harmful substances;
- air temperature;
- relative humidity;
- air velocity;
- dynamic pressure in the ducts.
Based on the results of the ventilation survey, a conclusion is issued on the sanitary-hygienic effectiveness of the system and recommendations for correcting deficiencies. Frequency of cleaning and disinfection:
- 1 time in 12 months - trade enterprises, public, office and administrative buildings;
- 1 time in 6 months - industrial buildings;
- 1 time in 3 months - cafes, restaurants, canteens, hospitals, clinics, medical centers;
- 1 time in 6 months - kindergartens, schools, institutes.
Disinfection of the ventilation system can be planned or according to the results of the examination. Disinfection is carried out after cleaning using special equipment.The solution disinfecting the ventilation system is applied to the inner surfaces of the ducts.
Fire hazard ventilation and measures to eliminate it
In industries associated with the penetration of explosive or combustible gases, dusts or vapors into the air, ventilation maintains a safe concentration. The fire hazard of ventilation systems is taken into account when calculating the intake and exhaust of air. If during the calculations and installation of mechanisms the fire hazard of the ventilation system is not taken into account, it can become a highway for the spread of fire.
Exhaust devices are placed so that dust or gas is removed directly from the place of emission, preventing the formation of conditions for fire. The source of fire hazard of the ventilation system can be the hot metal surfaces of the ducts and electric sparks that fall on combustible substances. Fire safety of ventilation systems is ensured by the following measures:
- fireproof ventilation equipment and materials are used, including for sealing joints, fixtures;
- fire damper equipment;
- air shutter equipment;
If it is not possible to equip fire dampers or valves, a separate ventilation system is installed for each room.
Video about the production of fire dampers: